To thrive in today’s competitive economy, your business needs every advantage it can muster.
What enters your business through your supply chain is as important as what goes out to your customers and clients—and to maximize your success, you need an effective and strategic method for handling your vendor relationships.
Proper vendor management balances maximizing value, building strong relationships, and supporting your company’s short- and long-term goals.
Depending on the size of your business, your purchasing organization might work with anywhere from a handful to hundreds of vendors, each with its own contract terms and pricing.
It might sound daunting, but with careful planning and strategic thinking, you can establish a winning management process for your vendors.
What is Vendor Management?
Vendor management is a systematic approach to managing and optimizing vendor relationships to ensure the smooth procurement of goods and services, favorable terms, and long-term partnerships.
This involves everything from selecting the right vendors to managing contracts, ensuring compliance, and evaluating performance.
What is a Vendor Management Process?
The vendor management process is the end-to-end methodology businesses employ to manage their vendors’ lifecycles.
It is part of the procurement process and is a comprehensive approach that includes identifying needs, selecting vendors, negotiating contracts, and managing ongoing relationships.
Cutting costs with lower price points and reduced spend is no longer enough to give your procurement organization, and your business as a whole, a serious competitive edge.
Effectively developing and maintaining strong relationships with third-party vendors is essential, as is maximizing the value your company receives from contracts through these relationships.
The vendor management process helps you achieve these goals through:
- Evaluating supplier capabilities, including turnaround times, pricing, and overall quality of goods and services
- Contract negotiation and payment confirmation
- Vendor relationship management
- Internal job assignments
- Ongoing performance evaluation via regular check-ins
Types of Vendor Management
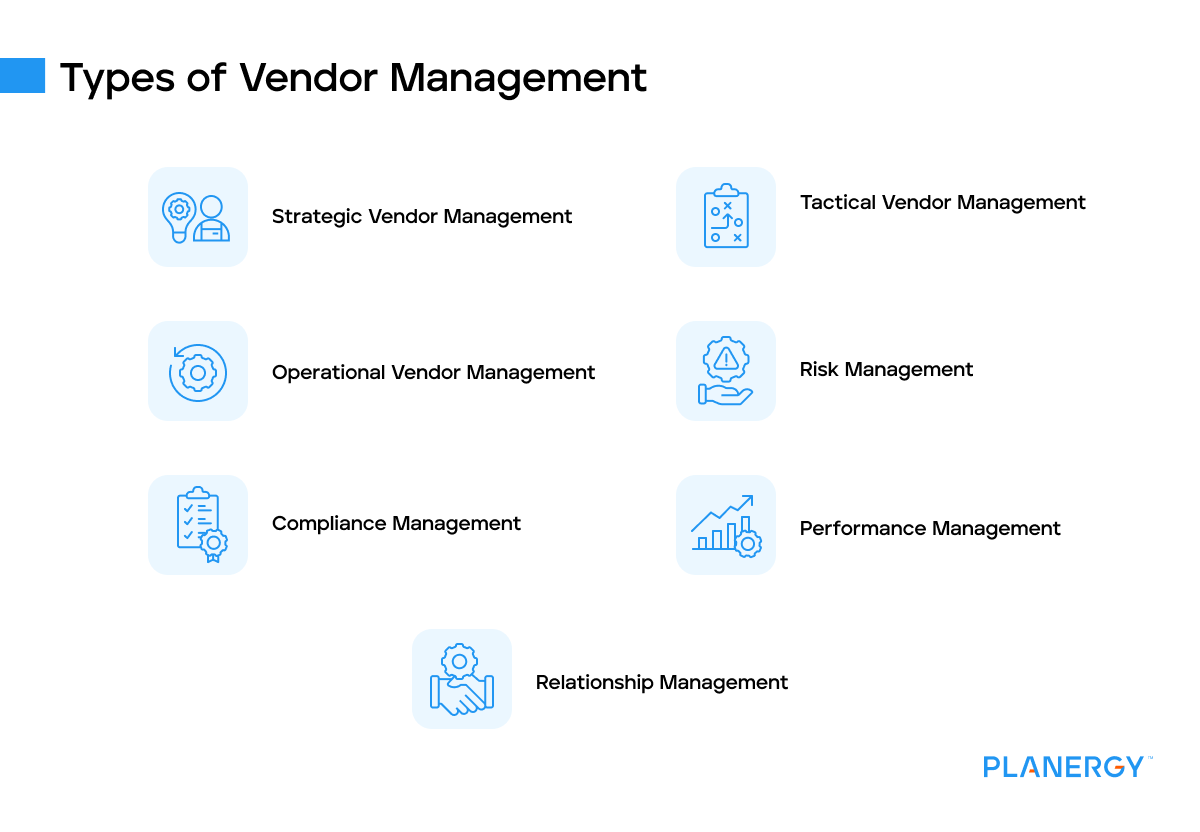
Strategic Vendor Management
Strategic vendor management focuses on building long-term relationships with key vendors that are critical to an organization’s success.
These vendors often provide essential goods or services that directly impact the company’s competitive advantage in the market.
The approach involves close collaboration, shared objectives, and, often, joint investments in projects or innovation.
The goal is to create a partnership that benefits both parties and aligns with the organization’s strategic direction.
Tactical Vendor Management
Tactical vendor management is more transactional and focuses on day-to-day vendor interactions.
It typically involves managing purchase orders, ensuring timely delivery of goods and services, and handling issues as they arise.
This type of management is often applied to vendors that provide non-critical, commoditized goods or services where the primary focus is efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reliability.
Operational Vendor Management
Operational vendor management concerns the operational aspects of vendor relationships, including contract administration, performance monitoring, and compliance with service level agreements (SLAs).
This type involves routine tasks such as reviewing vendor reports, conducting audits, and managing vendor databases.
It’s crucial to ensure that vendors meet their contractual obligations and deliver the expected value to the organization.
Risk Management
Vendor risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with vendor relationships.
This can include financial risks, operational risks, compliance risks, and reputational risks.
Organizations implement risk management strategies to protect themselves from potential negative impacts that could arise from vendor-related issues, such as supply chain disruptions, data breaches, or non-compliance with regulations.
Compliance Management
Compliance management focuses on ensuring that vendors adhere to industry regulations, legal requirements, and organizational policies.
This type of vendor management is particularly important in highly regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals.
It involves regular audits, assessments, and contract updates as laws and regulations change.
Performance Management
Performance management involves evaluating and improving vendor performance to meet or exceed predefined metrics and KPIs.
This approach involves setting clear expectations, continuously monitoring performance, and working with vendors to address any areas of concern.
The aim is to ensure that vendors consistently deliver high-quality goods and services that align with the organization’s objectives.
Relationship Management
Relationship management emphasizes building and maintaining positive relationships with vendors.
It involves regular communication, feedback, and problem-solving to foster a sense of partnership and collaboration.
Effective relationship management can lead to improved service levels, more favorable terms, and access to innovations that can benefit the organization.
Why is Vendor Management Important to Your Business?
Vendor management is the system your company uses to interface with external suppliers.
It covers everything from substantial investments like IT services and insurance to everyday goods and services.
Each vendor’s capabilities, reliability, and affordability can substantially impact your company’s bottom line.
Consequently, vendor relationship management (VRM) is effective risk management and an essential business process for building value and giving your company a competitive advantage in the long run.
What Are the Steps of the Vendor Management Process?
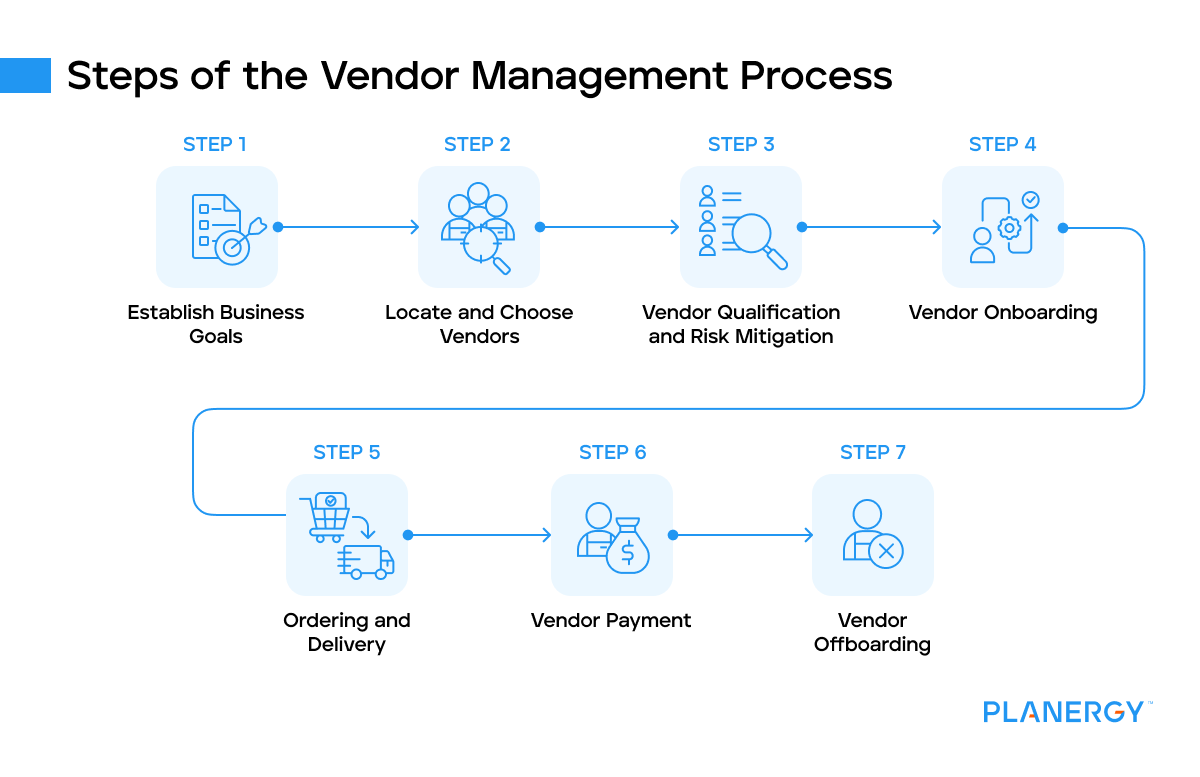
Establish Business Goals
The foundation of a successful vendor management process is the clear establishment of business goals.
Organizations need to define what they aim to achieve through their relationships with vendors.
These goals could range from cost reduction and improving service quality to ensuring timely delivery and fostering innovation.
By setting clear objectives, businesses can better identify the types of vendors they need to engage with to fulfill these goals.
Locate and Choose Vendors
Once goals are established, the next step is to locate and select the right vendors.
This involves conducting thorough market research to identify potential suppliers that can meet the organization’s needs.
Factors such as price, quality, reliability, and reputation play a crucial role in this selection process.
Businesses may also consider the vendor’s capacity for innovation and alignment with the company’s values and goals.
Vendor Qualification and Risk Mitigation
After identifying potential vendors, the next phase is vendor qualification and risk assessment.
This step involves evaluating the vendors’ capabilities and stability to ensure they can consistently meet your requirements.
Assessing risks associated with engaging a particular vendor is crucial to prevent supply chain disruptions and maintain quality standards.
This stage may include financial audits, reference checks, and evaluations of the vendor’s operational and compliance practices.
Vendor Onboarding
Following the selection and qualification of vendors, the onboarding process begins.
This step is critical for establishing a strong foundation for the vendor relationship.
It involves setting up legal contracts, integrating the vendor into your procurement and payment systems, and ensuring they understand your business processes and expectations.
Effective onboarding helps minimize misunderstandings and sets the stage for a smooth working relationship.
Ordering and Delivery
With the vendors onboarded, the focus shifts to ordering and delivering goods or services.
This step requires clear communication of orders, timelines, and quality expectations.
Systems to track orders and manage any issues that arise during this phase are also essential.
Efficient processes for ordering and delivery contribute to the smooth operation of the supply chain and help maintain positive vendor relationships.
Vendor Payment
Timely and accurate payment is a critical component of vendor management.
This step involves processing invoices, resolving discrepancies, and making payments according to the agreed-upon terms.
Efficient vendor payment processes strengthen trust and reliability between parties, contributing to long-term partnerships.
Vendor Offboarding
The final step in the vendor management process is vendor offboarding. This may occur when a contract ends, a vendor’s performance is unsatisfactory, or business needs change.
Offboarding involves concluding outstanding obligations, retrieving assets, and ensuring a smooth transition.
Properly managing this phase helps maintain professional relationships and leaves the door open for future engagements if circumstances change.
Challenges of Effective Vendor Management
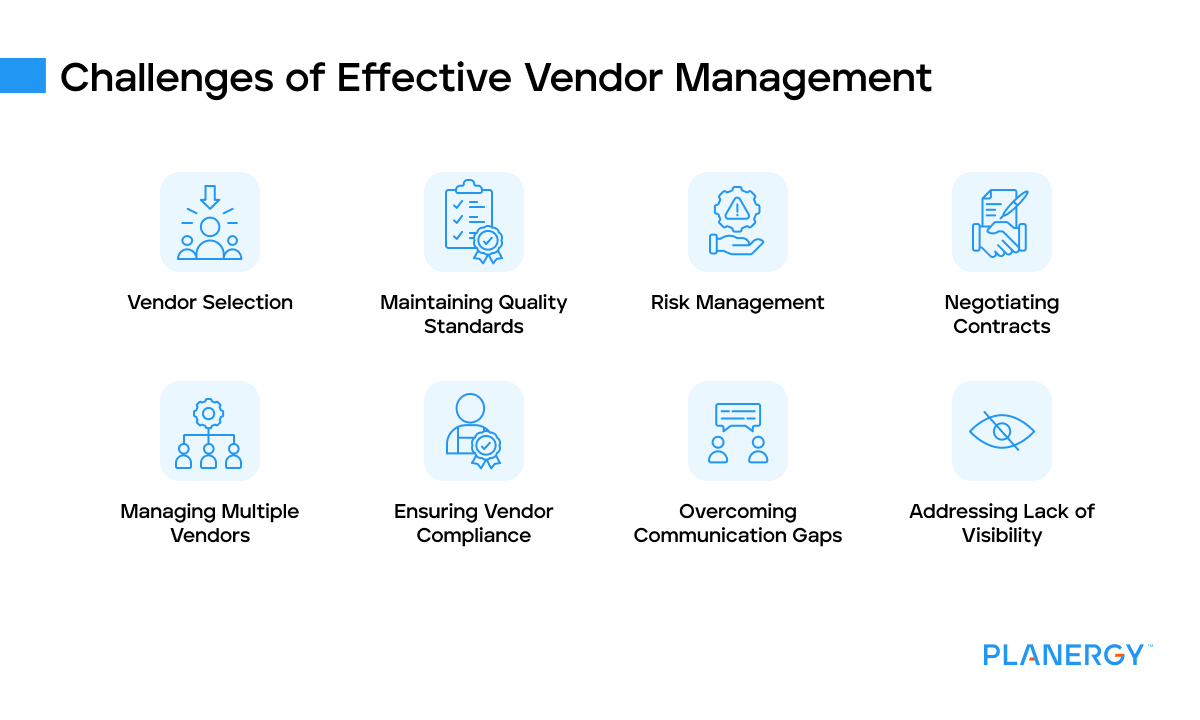
Vendor Selection
One of the initial hurdles in the vendor management process is identifying and selecting the right vendors that align with your business objectives.
The challenge lies in thoroughly vetting potential vendors for their capability, reliability, financial stability, and compatibility with your organizational culture and needs.
Making the wrong choice can lead to subpar service, supply chain disruptions, and increased costs.
Maintaining Quality Standards
Ensuring that vendors consistently meet agreed-upon quality standards is another significant challenge.
This requires establishing clear expectations, continuous monitoring, and effective communication to address any issues promptly.
However, maintaining these standards can be difficult, especially when dealing with multiple vendors or when vendors are located in different geographic regions with varying regulatory environments.
Risk Management
Vendor relationships inherently carry risks, including operational, financial, compliance, and reputational risks.
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating these vendor risks is crucial but challenging.
This involves conducting due diligence before onboarding vendors, continuously monitoring their performance, and having contingency plans to manage potential issues.
Negotiating Contracts
Negotiating favorable contract terms that protect your interests while maintaining a good relationship with the vendor can be complex.
Contracts must be clear, comprehensive, and flexible enough to accommodate changes.They should cover pricing, delivery schedules, confidentiality, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Achieving a balance that satisfies both parties requires skillful negotiation and a deep understanding of your business needs and the vendor’s capabilities.
Managing Multiple Vendors
Organizations often work with many vendors simultaneously, complicating vendor management efforts.
Keeping track of different contracts, performance metrics, compliance requirements, and communication channels for each vendor demands significant time and resources.
It also increases the likelihood of errors and oversight, making effective management complex.
Ensuring Vendor Compliance
Ensuring vendors comply with industry regulations, legal requirements, and your company’s internal policies is essential but challenging.
Compliance requires regular audits, assessments, and contract updates as laws and regulations change.
Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, damage to reputation, and financial loss.
Overcoming Communication Gaps
Effective communication between your organization and its vendors is key to a successful partnership.
However, communication gaps often occur due to differences in time zones, language barriers, cultural differences, or misaligned expectations.
These gaps can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and dissatisfaction.
Addressing Lack of Visibility
A lack of transparency and visibility into vendor operations, performance, and spend can hinder effective vendor management.
Without accurate and timely information, it’s challenging to make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, or detect potential issues before they escalate.
Benefits of Tracking Vendor Performance
![]()
Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings
An effective vendor management process can significantly improve administrative efficiency.
By streamlining vendor selection, onboarding, and payment procedures, businesses can reduce manual efforts and associated costs.
Moreover, a well-structured process allows for better contract and terms negotiation, potentially leading to cost savings on goods and services.
Enhanced Vendor Relationships
Building strong relationships with vendors is pivotal for long-term business success.
A systematic approach to vendor management fosters clear communication and collaboration, establishing a foundation of trust and mutual respect.
This can lead to more favorable terms, improved service quality, and access to additional benefits such as priority support or exclusive offerings.
Reduced Risks
Vendor management processes help identify and mitigate risks associated with vendor relationships.
Businesses can address potential issues before they escalate by conducting thorough due diligence and ongoing performance monitoring, reducing the risk of supply chain disruptions, compliance violations, and reputational damage (Volopay).
Streamlined Processes and Less Paperwork
A structured vendor management system simplifies various administrative tasks, reducing the need for paperwork and manual record-keeping.
This saves time and minimizes errors and inefficiencies associated with handling multiple vendor contracts and negotiations.
As a result, organizations can allocate resources more effectively toward core business activities.
Increased Visibility and Control
Implementing a vendor management process gives businesses greater visibility into their vendor relationships, including performance metrics, financial commitments, and compliance status.
This enhanced oversight enables decision-makers to exercise better control over vendor-related activities, ensuring that they align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Access to Innovation and Market Advantages
By nurturing strong vendor relationships, companies can access the latest innovations and market opportunities.
When leveraged through collaborative partnerships, vendors often possess unique insights and capabilities to drive competitive advantage and support business growth.
Loyalty and Long-Term Partnerships
Effective vendor management contributes to loyalty between organizations and their vendors.
Over time, this loyalty can evolve into long-term partnerships, wherein vendors are more likely to go above and beyond to meet your needs, offer better terms, and provide strategic support to help you achieve your business goals.
Best Practices for Implementing a Solid Vendor Management Program

Enforce a Clear Vendor Management Policy
A foundational step in establishing effective vendor management is creating and enforcing a clear vendor management policy.
This policy should outline the procedures for selecting, onboarding, managing, and evaluating vendors. It is a guideline for your team and the vendors, ensuring consistency and clarity in managing relationships.
A well-documented policy helps mitigate risks and sets clear expectations for performance and compliance.
Choose the Right Vendors for Your Business
It is crucial to select vendors that align with your business needs and values.
This involves thoroughly assessing potential vendors’ capabilities, reliability, financial stability, and compatibility with your company’s culture and objectives.
Choosing the right vendors impacts the quality of goods and services. It plays a significant role in the efficiency of your supply chain and the overall success of your vendor management strategy.
Conduct Due Diligence for Vendors
Conducting comprehensive due diligence is essential before finalizing any new vendor agreements.
This process includes verifying the vendor’s references, reviewing their financial health, assessing their operational capabilities, and ensuring they comply with relevant laws and regulations.
Due diligence helps identify potential risks and issues early in the relationship, allowing for informed decision-making and risk mitigation strategies.
Develop Robust Vendor Partnership Evaluation
To maximize the value of your supplier relationships, it is important to develop a robust framework for evaluating vendor partnerships.
This includes setting clear performance metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with your business objectives.
Regularly assessing vendors against these metrics enables continuous improvement, fosters accountability, and ensures that vendors remain aligned with your strategic goals.
Nurture the Relationship
Building and maintaining strong long-term relationships with your vendors is key to achieving successful outcomes.
Regular communication, transparency, and collaboration are vital components of this practice.
Treating vendors as strategic partners can create a mutually beneficial environment that encourages innovation, flexibility, and commitment to shared goals.
Educating vendors about your business strategy while learning about theirs can uncover new opportunities for value creation and efficiency improvements.
Centralize Vendor Management Practices
Centralizing vendor management practices within your organization can improve oversight, consistency, and control over vendor relationships.
This may involve utilizing dedicated vendor management software or platforms to manage vendor information, contracts, performance data, and communications.
A centralized approach ensures vendor-related decisions are informed by comprehensive, up-to-date information and align with broader organizational strategies.
Outline Clear Expectations and Communication Channels
Clear communication is the cornerstone of effective vendor management. It’s important to establish and maintain open lines of communication and to outline clear expectations for both parties from the outset.
This includes specifying deliverables, timelines, quality standards, and reporting requirements.
Effective communication helps prevent misunderstandings, resolves issues more efficiently, and strengthens the partnership between your organization and its vendors.
Improving Vendor Management
Organizations can improve their vendor management processes by leveraging technology solutions like PLANERGY.
These solutions offer features for automating and streamlining tasks, managing contracts, and analyzing supplier performance KPIs.
These tools save time and provide valuable insights into vendor data for making informed decisions.
Better Vendor Relationship Management and Performance Management
An effective vendor management process is instrumental in building strong, productive relationships with vendors.
By understanding its importance, implementing robust processes, and utilizing vendor management system (VMS) technology to enhance efficiency, organizations can achieve significant benefits across the board.