As a procurement professional, you know the importance of ensuring that all materials and services delivered by vendors meet or exceed your standards for quality and performance.
That’s why vendor analysis is essential to any successful procurement process – it helps ensure that companies procure from reliable suppliers at competitive prices while adhering to applicable regulations.
In this blog post, we’ll explore vendor analysis, its underlying processes and types, and best practices when implementing this critical tool in your organization.
Read on to learn more about how effective vendor analysis can help you streamline your supply chain management efforts!
What is Vendor Analysis?
Vendor analysis evaluates and compares various suppliers based on their pricing, quality, reputation, reliability, and service delivery.
It’s an essential tool for businesses to identify the best suppliers for your business needs, and build strong, long-term partnerships with them.

This is usually incorporated into the broader supplier evaluation and selection process when onboarding new suppliers. But it will also be incorporated into regular supplier reviews to consider if they are still the right preferred vendor for the company to use.
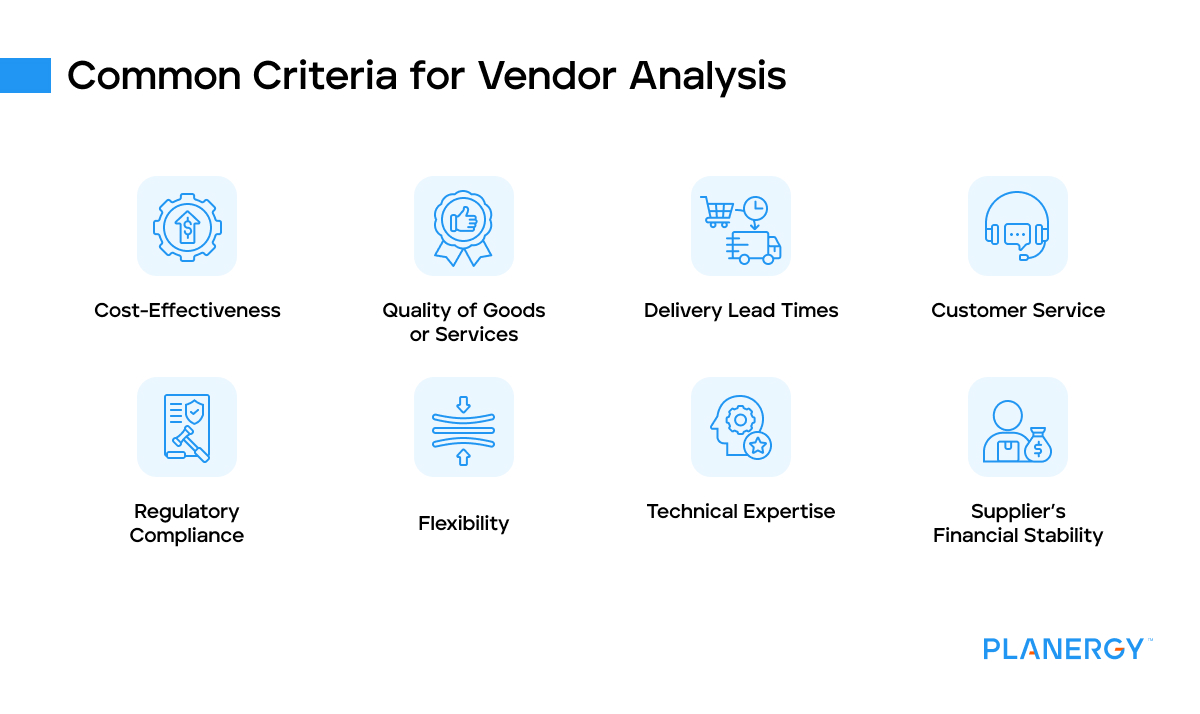
The criteria used in vendor analysis can vary depending on the business’s needs.
Common factors include cost-effectiveness, quality of goods or services, delivery lead times, customer service, regulatory compliance, flexibility, technical expertise, and the supplier’s financial stability.
What is a Vendor Analysis Report?
A vendor analysis report is a document that summarizes the findings of the vendor analysis process. It typically includes information about the supplier’s strengths and weaknesses, potential risks, and opportunities for improvement.
What Does a Vendor Analyst Do?
A vendor analyst is responsible for conducting the vendor analysis. Their role involves researching potential suppliers, analyzing their offerings, and making recommendations to the business based on their findings. Vendor analysts are the people who conduct due diligence.
What Is Vendor Due Diligence?
Vendor due diligence refers to the process of investigating a supplier before entering into a business agreement with them. It’s crucial to ensure that the supplier can fulfill their obligations and that they align with your company’s values and goals.
Due diligence can help uncover potential issues, such as financial instability or legal troubles, that could impact the supplier’s ability to deliver.
It also provides valuable insights into the supplier’s operations, which can inform negotiation strategies and decision-making.
Vendor Analysis vs. Vendor Assessment
While both vendor analysis and vendor assessment aim to evaluate suppliers, there are slight differences between the two.
Vendor analysis is a more comprehensive process that involves a detailed evaluation of various aspects of a supplier.
On the other hand, a vendor assessment is usually a narrower process that focuses on assessing a supplier’s performance against specific criteria or standards.
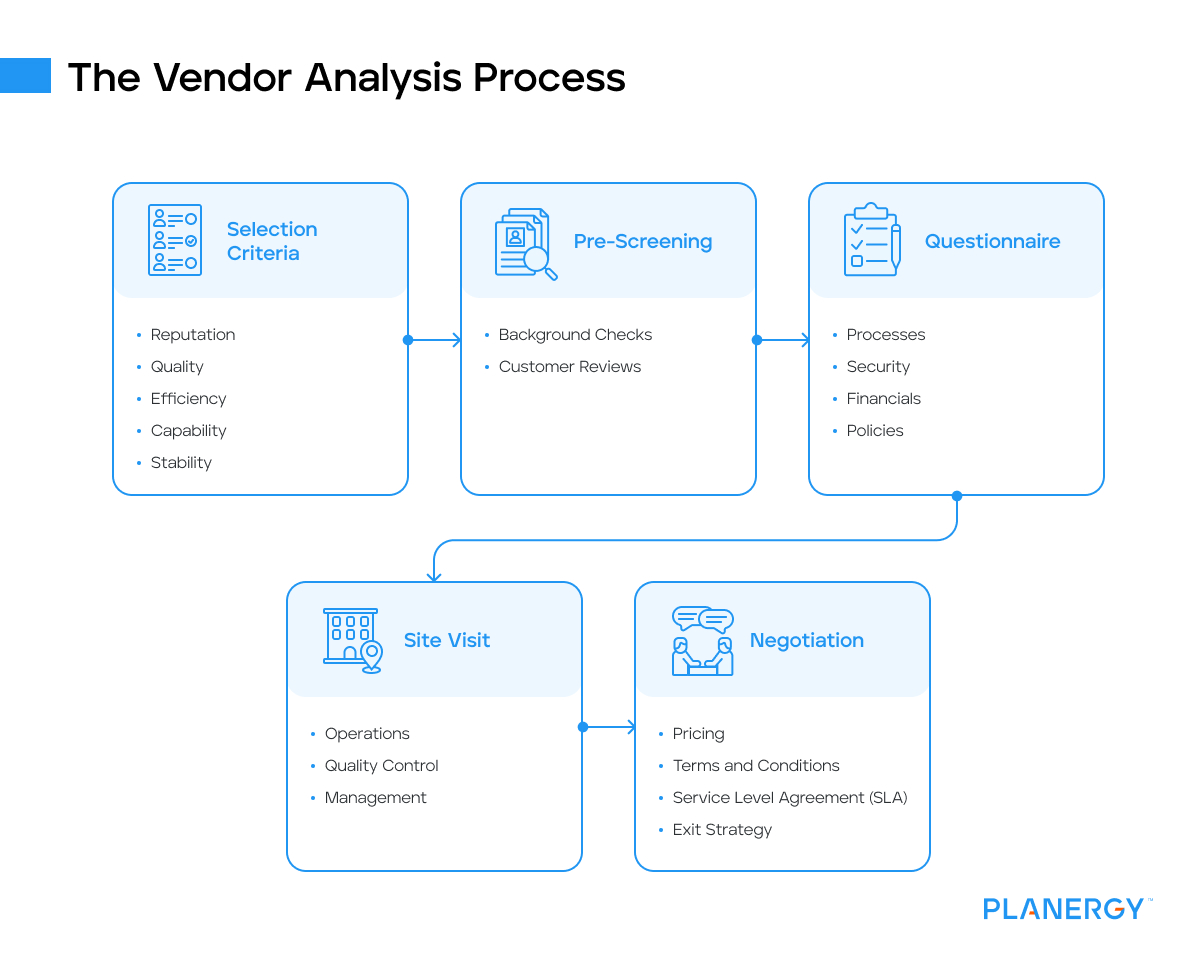
The Vendor Analysis Process
This is a multi-step, in-depth business process designed to help you find the best vendor for your needs.
Selection Criteria
The selection criteria stage is where businesses identify potential vendors based on several factors:
- Reputation: Look at online reviews, ratings, and feedback from other customers.
- Quality: Assess the quality of products or services the vendor offers.
- Efficiency: Evaluate how efficiently the vendor can deliver their products or services.
- Capability: Determine if the vendor has the capacity to meet your business’s demands.
- Stability: Examine the vendor’s financial health to ensure stability and reliability.
Pre-Screening
Pre-screening is a preliminary step to narrow down potential suppliers:
- Background Checks: Conduct a thorough background check on the vendor. This includes checking their legal history, financial records, and media coverage.
- Customer Reviews: Review experiences from existing customers. This can provide valuable insights into the vendor’s reliability, customer service, and product quality.
Questionnaire
A questionnaire can help businesses get detailed information about the vendor’s operations:
- Processes: Ask about the vendor’s production processes, delivery timelines, and quality control measures.
- Security: Inquire about the vendor’s security protocols, especially if they handle sensitive data.
- Financials: Ask for details about the vendor’s financial stability, including their credit rating and financial statements.
- Policies: Understand the vendor’s policies on issues like returns, refunds, and customer service.
Based on the information you collect about your prospective vendors, you can create a shortlist of specific vendors you want to investigate further. Narrow it down to a few providers before moving to the next step.
Site Visit
A site visit allows businesses to get a firsthand look at a vendor’s operations:
- Operations: Observe the day-to-day operations of the vendor. This can give you an idea of their efficiency, organization, and work culture.
- Quality Control: Check the vendor’s quality control measures. This can include inspecting their facilities, equipment, and processes.
- Management: Meet with the vendor’s management team. This can provide insights into their leadership style and business philosophy.
Once you finish the site visits, you can move into narrowing down the list even further based on your findings. When you find a vendor or two that you’re most interested in working with, move into the negotiation phase.
Negotiation
The negotiation phase is where businesses discuss terms with the vendor:
- Pricing: Discuss pricing options. Aim for a price that is fair for both parties and sustainable in the long term.
- Terms and Conditions: Review the vendor’s standard terms and conditions. Negotiate changes if necessary to protect your business’s interests.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): Define the level of service you expect from the vendor. This should include specifics about delivery times, quality standards, and response times for issues or queries.
- Exit Strategy: Discuss what will happen if the relationship needs to end. This should cover scenarios such as contract termination, transition of services, and resolution of outstanding issues.
At the end of the negotiation phase, you should know which vendor you want to enter into a contract with.

Vendor evaluation is an important part of the process for all projects – because you want vendors who can meet your needs, and have the financial strength to stay in business a long time.
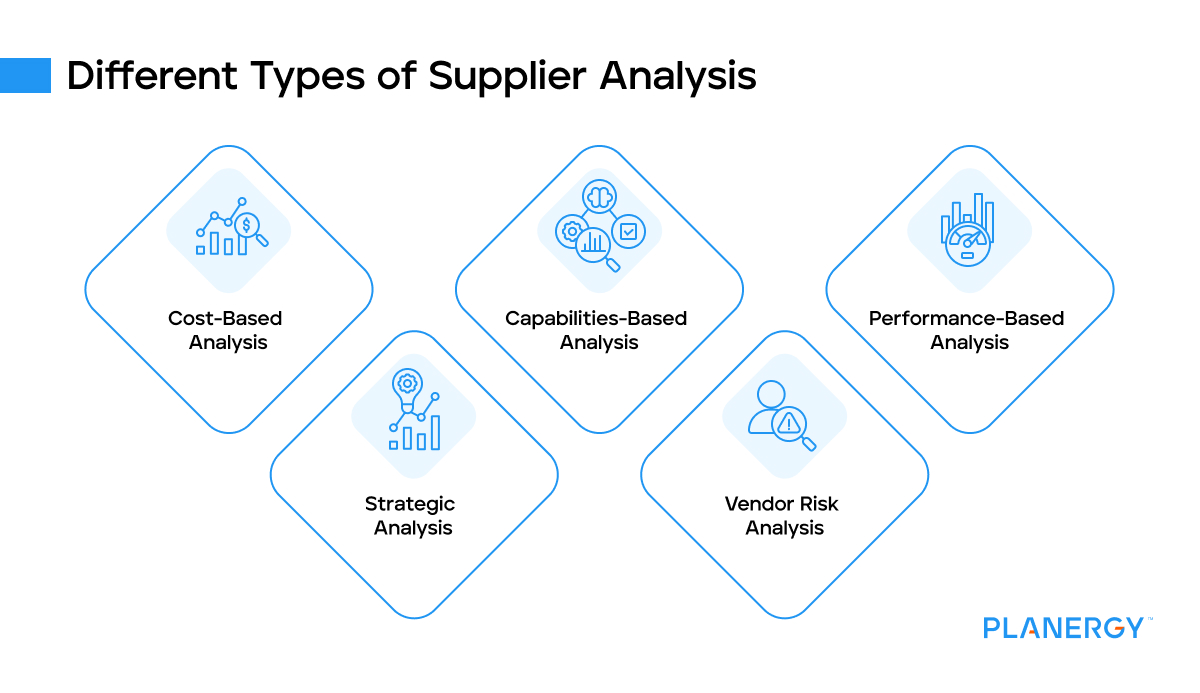
Different Types of Supplier Analysis
There are different types of vendor analysis, each with its unique focus. For instance, a cost-based analysis looks at the supplier’s pricing structure, while a capabilities-based analysis evaluates the supplier’s ability to meet specific requirements.
Cost-Based Analysis
A cost-based analysis concentrates on the financial aspects of the deal, including suppliers’ pricing models, payment terms, and potential discounts or rebates.
It helps identify if a supplier is offering value for money and aids in comparing different suppliers’ pricing strategies.
Capabilities-Based Analysis
This analysis assesses a supplier’s ability to meet the specific needs of a business. This could include production capacity, technological capabilities, compliance with industry standards, and ability to meet delivery deadlines.
Performance-Based Analysis
This type of analysis evaluates a supplier’s past performance. It considers factors like delivery punctuality, error rate, responsiveness to issues, and overall reliability.
This is a good way to monitor how well a vendor meets your needs after working with them for a few months.
Strategic Analysis
This analysis looks at a supplier’s strategic value to the business. It evaluates the potential for a long-term relationship, the supplier’s position in the market, and the risk and opportunities associated with the supplier.
Vendor Risk Analysis
This analysis identifies potential risks associated with a supplier. These could be financial, operational, reputational, compliance-related, or supply chain risks. It’s crucial to ensure the business is prepared for any negative impacts a supplier could have.

Each type of vendor analysis provides valuable insights, and businesses often employ a combination of these to make the most informed decisions.
Best Practices for Effective Vendor Analysis
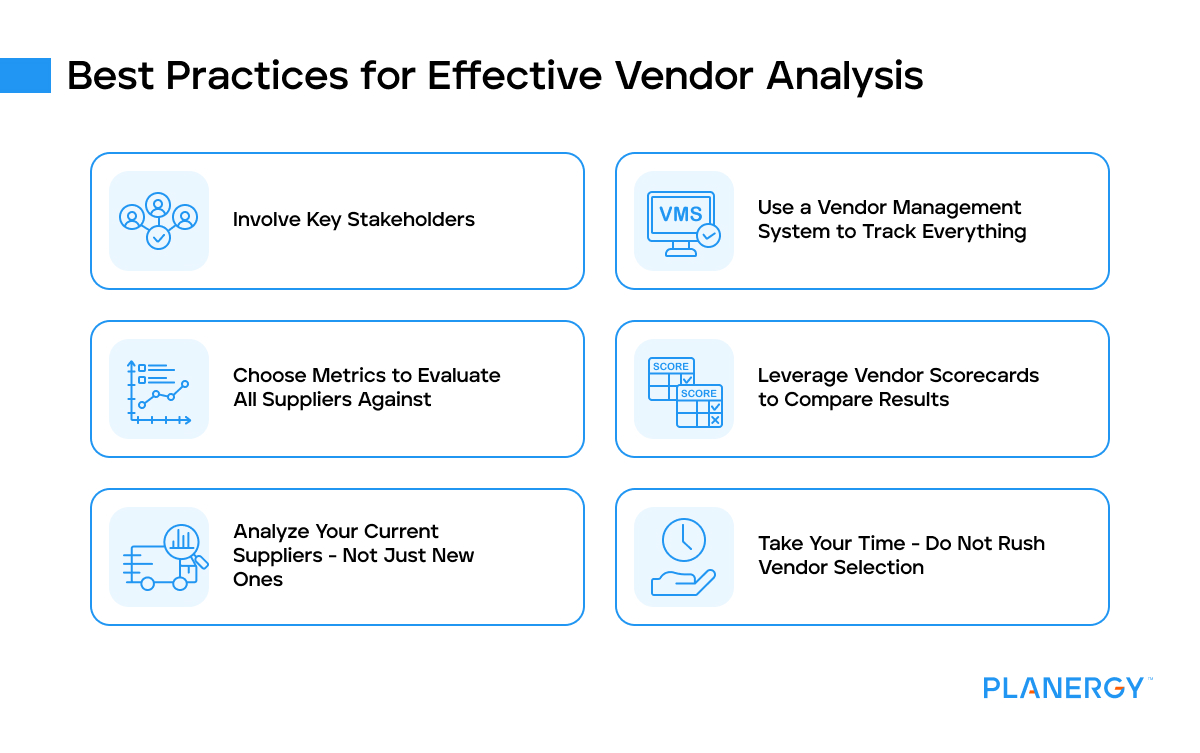
Involve Key Stakeholders
Involving stakeholders in the vendor selection process is not just important; it’s crucial for the success of any business project.
Stakeholders can include anyone who has an interest in the project or will be affected by its outcome, such as employees, managers, customers, and investors.
Each stakeholder brings a unique perspective and set of expertise to the table, which can greatly enhance the decision-making process.
Including stakeholders in vendor selection ensures that all relevant viewpoints are considered. For instance, while a procurement team might focus on cost, a product manager may prioritize quality, and a customer service representative might emphasize reliability.
By incorporating these diverse perspectives, businesses can make more informed and balanced decisions aligning with their strategic objectives.
Involving stakeholders also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the project. When stakeholders are part of the decision-making process, they are more likely to support and actively contribute to successfully implementing the chosen vendor solution.
This cross-functional collaborative approach can lead to better project outcomes, increased stakeholder satisfaction, and stronger vendor relationships.
Use a Vendor Management System to Track Everything
A vendor management system (VMS) can be an invaluable tool in managing supplier performance reviews and maintaining relationships.
This system provides a centralized platform where all relevant procurement and vendor data about a supplier’s performance can be stored, tracked, and analyzed.
Vendor management key performance indicators such as delivery times, quality of goods or services, responsiveness to issues, and cost-effectiveness can be monitored in real-time, providing you with actionable insights into each supplier’s performance.
To conduct a supplier performance review using a VMS, set up the key metrics that matter most to your business.
The system will then continually track these metrics, providing real-time updates. When it’s time for a review, the VMS can generate comprehensive reports detailing the supplier’s performance, highlighting areas of strength and those needing improvement.
But a VMS isn’t just for tracking and reviewing performance; it’s also a powerful tool for maintaining and enhancing supplier relationships.
Providing transparent feedback based on concrete data encourages open communication between you and your suppliers. You can work together to address any issues, improve performance, and optimize processes.
Moreover, recognizing and rewarding high-performing suppliers can strengthen relationships and foster long-term partnerships. In this way, a VMS can play a pivotal role in managing and enhancing your supplier relationships.
Choose Metrics to Evaluate All Suppliers Against
Choosing the right metrics to evaluate your suppliers is the first step toward effective supplier management.
These metrics allow you to objectively measure and compare supplier performance, helping you identify the best suppliers for your business.
What you choose will depend on your business model and goals, what product or service you’re trying to procure, and the type of analysis you’re conducting.
These metrics are important because they directly impact your business’s ability to provide high-quality products or services to your customers.
However, the importance of each metric may vary depending on your business’s specific needs and goals and the nature of your industry.
Leverage Vendor Scorecards to Compare Results
Vendor scorecards are a powerful tool for evaluating and comparing suppliers. They provide a standardized format for collecting and displaying data on various qualitative supplier performance metrics, enabling you to quickly and easily assess supplier performance.
A vendor scorecard might include data on:
Product or Service Quality
Measured by defect rates, specifications compliance, and customer feedback.
Delivery Performance
Measured by factors such as on-time delivery rate, order accuracy, and flexibility in handling changes or emergencies.
Cost Competitiveness
Measured by factors such as price competitiveness, cost savings achieved, and payment terms.
Customer Service
Measured by factors such as response time, problem resolution efficiency, and communication quality.
Using vendor scorecards has several advantages over other supplier evaluation methods.
It provides a clear, visual representation of supplier performance, makes it easy to compare different suppliers, and allows for ongoing tracking of supplier performance over time for easier and faster decision-making.
Analyze Your Current Suppliers – Not Just New Ones
While it’s important to thoroughly evaluate potential new vendors, it’s equally important to continuously analyze your existing suppliers.
This helps ensure that they continue to meet your performance standards and allows you to address any issues before they become significant problems.
Regular supplier analysis can involve:
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of supplier performance based on your chosen metrics.
- Feedback Sessions: Provide feedback to suppliers on their performance and discuss any areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement Plans: Work with suppliers to develop and implement plans for continuous improvement.
Take Your Time – Do Not Rush Vendor Selection
Choosing the right vendor is not just about finding the most cost-effective solution; it’s about ensuring that you receive high-quality services that meet your specific needs and contribute positively to your business’s overall productivity and efficiency.
Rushing into vendor selection without proper due diligence can lead to subpar results, increased business risks, and potential losses in the long run.
Vendor Performance and Evaluation Can Make or Break Your Business
Regularly evaluating supplier performance is an essential part of any successful business.
It helps identify improvement areas, provides insight into how the vendor can better meet your needs and can improve long-term supplier relationships.
Regular evaluations should be performed by a knowledgeable individual familiar with the services being provided. The evaluation should include feedback from multiple departments or sources to ensure that all relevant data is considered.