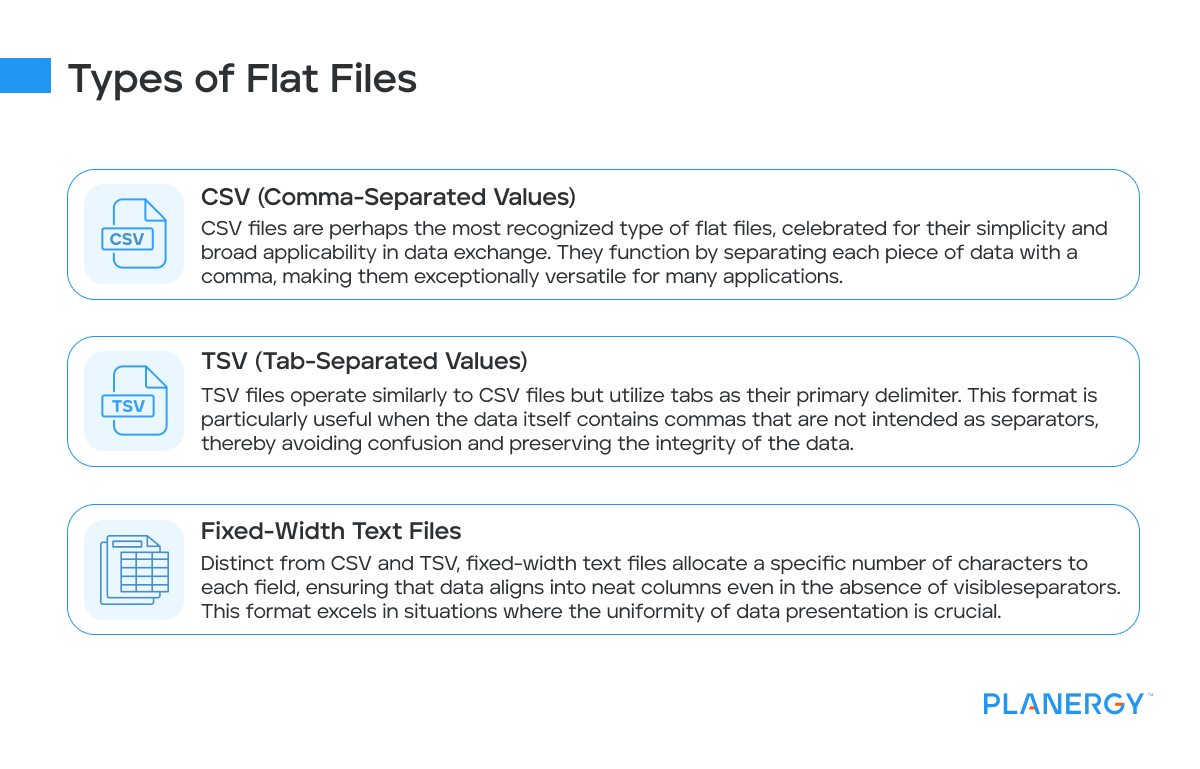
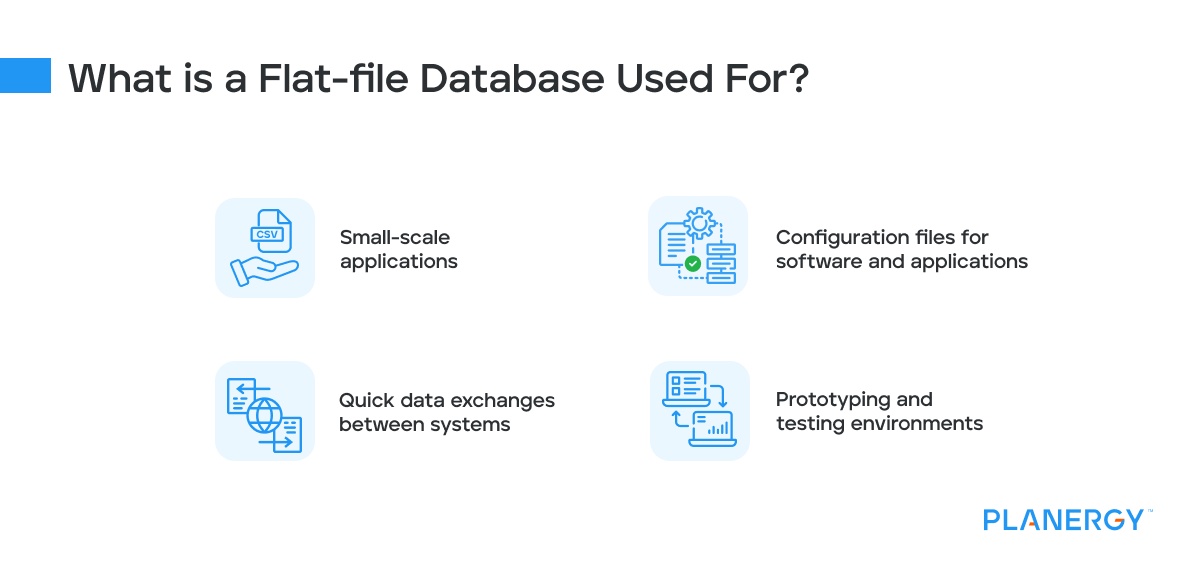
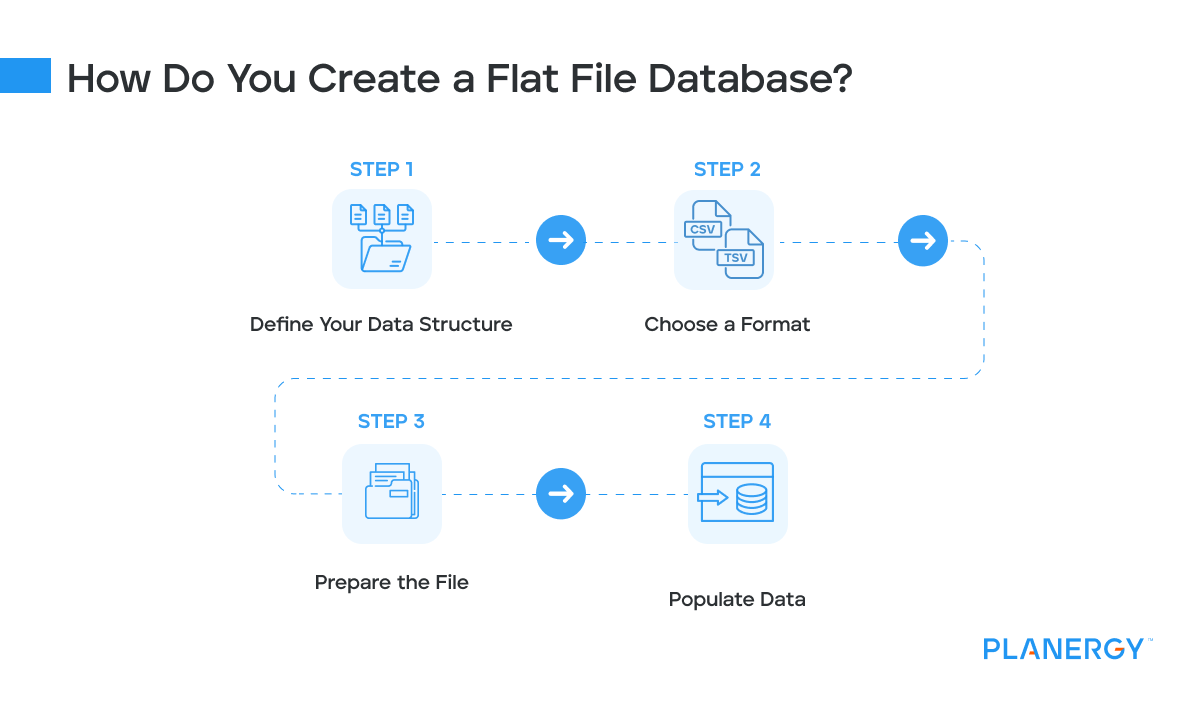
What is a Flat File?
A flat file is a plain text file or binary file that lacks a strict schema that stores data in a tabular format. Imagine it as a single, extensive table where each line represents a record, and each field is separated by a delimiter, such as a comma, tab, or space.
These files are incredibly straightforward, making them accessible and easily editable with basic tools like a text editor.
Microsoft Word (stored in a plain text file format), Microsoft Excel, JSON files, all use flat data files.
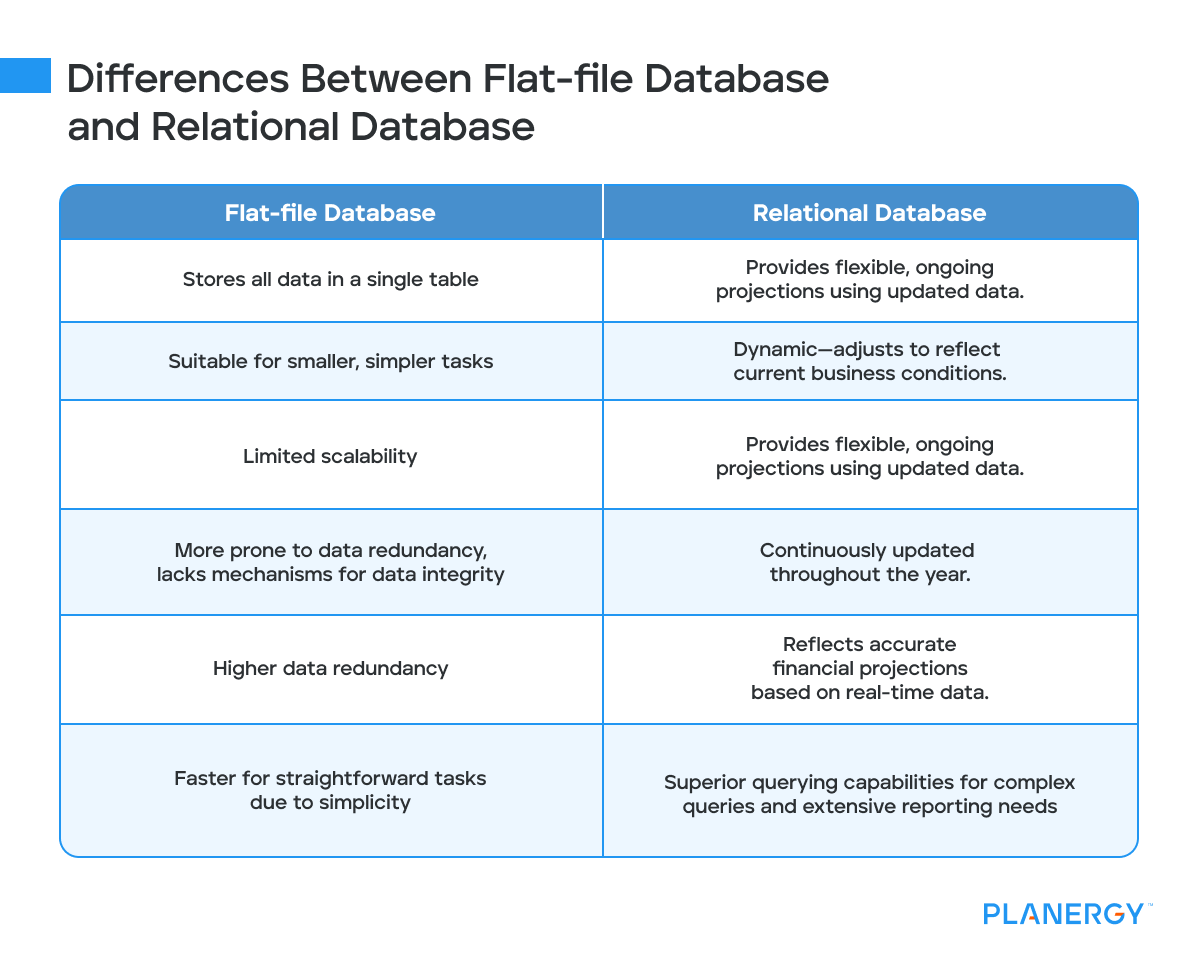
Each column in a flat file database is restricted to a specific data type, such as phone numbers. Everything is stored in a single record.
The delimiters keep the data formatting at a fixed width and make finding different fields within a record easier.
The first row in a flat file refers to the field name – which makes it easier to determine what data is dealt with in each field.
All the rows in the flat file database follow the tuple concept in relational algebra, where tuples are an ordered list of elements.
Data in flat files remains in its original form until it is transferred into a staging area in a warehouse or a database management system. After the transmission is complete, the data is altered and saved in different forms.
Linux, Windows, and Macintosh operating systems run on a flat file system. Flat file databases are also easy to use for storing customer lists and business contacts.
However, if you have more than a few thousand records, they can have some disadvantages.
They can be harder to update, contain non-unique records, have increased potential for duplication, and, over time, become inefficient.