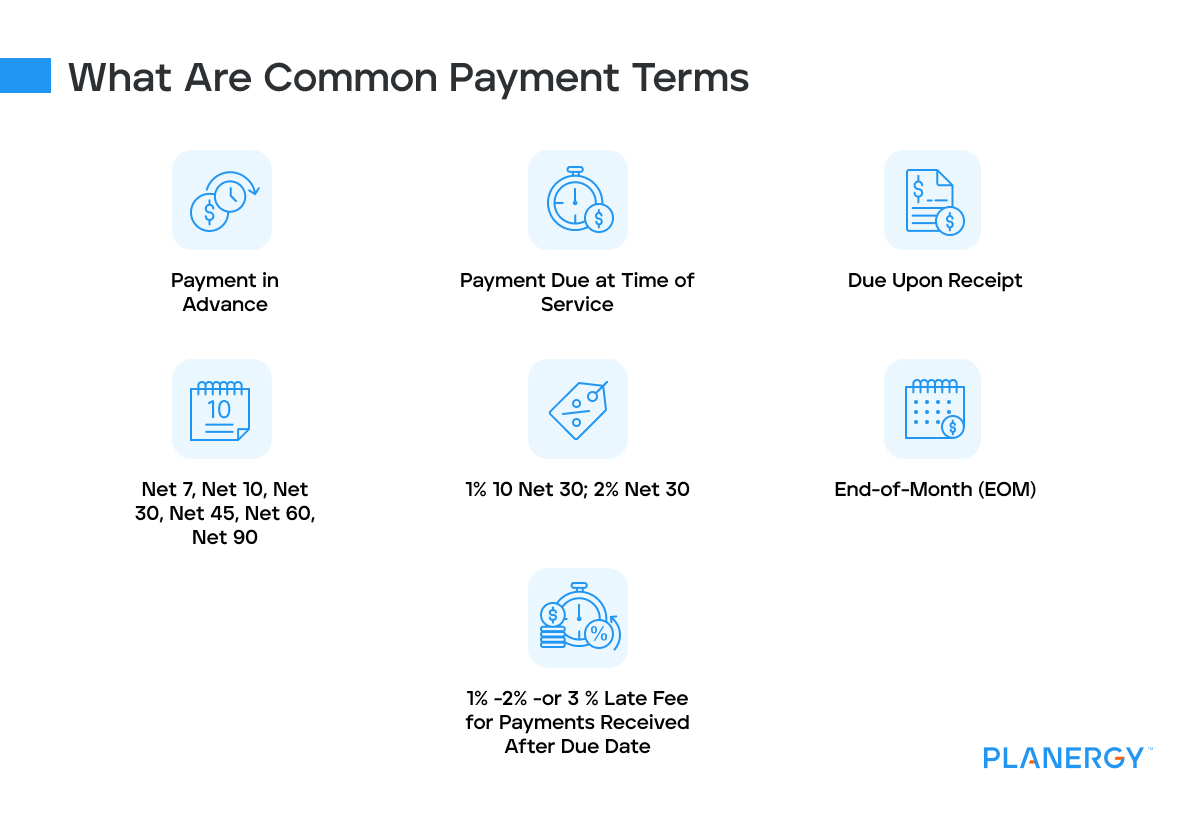
Business owners have numerous choices when it comes to setting payment terms for their customers, with each of the terms having advantages and disadvantages.
Payment in Advance
Payment in advance is typically used for special orders or large construction projects where there is a significant monetary investment on the part of the business before the project or service can begin.
Though some customers may balk at having to pay a deposit upfront, businesses that perform custom work can end up losing a lot of money should the customer not follow through on the order.
Payment in advance is also common when dealing with customers with bad credit or no credit.
Payment Due at Time of Service
Payment due at the time of service is similar to payment in advance but instead of a deposit, immediate payment is expected at the time goods are received or services rendered.
Payment due at time of service is also known as cash on delivery, or COD.
Due Upon Receipt
Due upon receipt indicates that payment is due when the customer receives the invoice.
Again, businesses with limited cash flow that want to sell on credit may use this payment term, since it’s trusting the customer to pay, but requires payment immediately upon invoice receipt.
In most cases, due upon receipt payments are due by close of business the following business day.
Net 7, Net 10, Net 30, Net 45, Net 60, Net 90
Net terms indicate the number of days from the date of the invoice that payment is due.
For example, if your invoice date is November 20 and the invoice terms are Net 30, the customer is expected to pay the invoice by December 19.
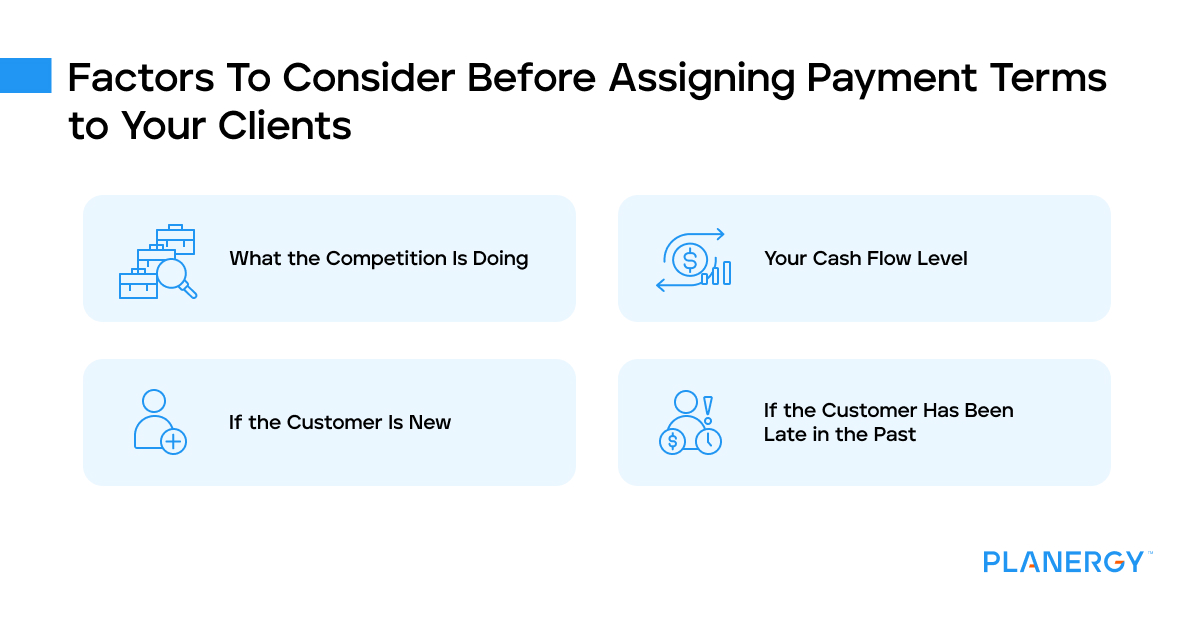
While some small businesses use the same term for all customers, many businesses assign terms based on each customer.
For example, businesses may assign Net 7 or Net 10 terms to newer customers to see how quickly payment is received while terms for long-time or prompt-paying customers may be more relaxed.
1% 10 Net 30; 2% Net 30
Some businesses may provide an early payment incentive to their customer by offering a small discount if the business pays early, usually within 10 days from the date of the invoice. 1% Net 30 means that if your customer pays you within 10 days of the invoice date, they are entitled to take a 1% discount off the total of the invoice.
If they don’t pay within 10 days, they will need to pay the entire invoice amount within 30 days from the invoice date.
If the terms are 2% Net 30, they can take a 2% discount off of the invoice total, with the same requirement to pay the full amount within 30 days.
End-of-Month (EOM)
End-of-month invoice terms aren’t commonly used.
EOM payment terms mean that the total amount due is payable at the end of the month regardless of when the invoice was issued.
1% -2% -or 3% Late Fee for Payments Received After Due Date
If you intend to charge your customers a late fee when a payment is past due, the late fee notice should be included in the payment terms on the invoice.
For example, if your terms are Net 30, but you’re charging 2% interest on late payments you can include that as a message on the invoice:
Please note that payment is due within 30 days. A monthly late fee of 2% of the amount due will be charged on any overdue payments.
Any late fees should also be spelled out on any contract or agreement you have with your customers. Most late fees range from 1% to 3%.
Businesses also have the option to charge a flat fee when a payment is late.
For more information on late fees and restrictions, it’s best to check with your local or state laws governing late fees.