Whether you’re a Fortune 500 company or a sole proprietor, we all go into business with a specific goal in mind; to sell products and services to customers.
Part of the role of being an entrepreneur is accurately predicting what customers want, both now and in the future, and then later using those predictions to make more informed decisions.
These predictions are completed using demand forecasting, also known as demand planning.
What Is Demand Forecasting?
Demand forecasting uses past data and other financial metrics to accurately predict customer demands for the future.
Demand forecasting can be completed on existing products and services as well as those not yet introduced.
As an example, demand forecasting proved valuable during the recent pandemic as companies struggled to determine demand levels for high-ticket items such as automobiles.
Most accurate when completed on a single product or service, using the demand forecasting process can help companies better strategize for the future.
Types of Demand Forecasting Techniques and Methods
If you’re interested in forecasting demand, there are numerous demand forecasting techniques and methods available to use.
Not all techniques and/or methods are suitable for all businesses, so making the proper decision on which model or method to use is essential.
Demand Forecasting Techniques
There are several demand forecasting techniques that can be used to create a demand forecast.
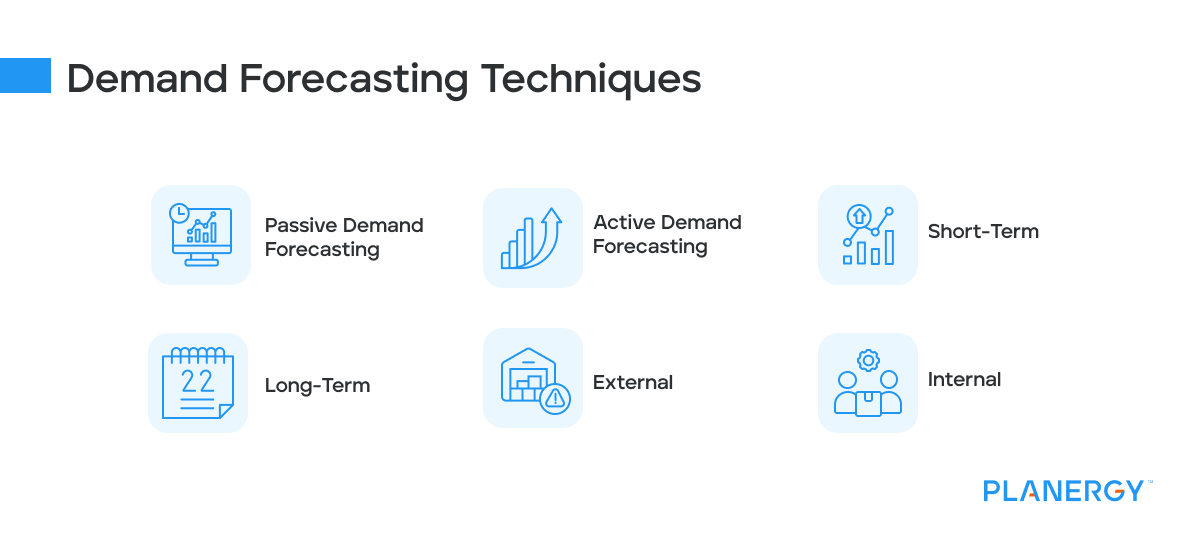
Passive Demand Forecasting
The passive type of demand forecasting uses past data to predict future results.
The simplest demand forecasting model, the passive model can be used to consistently predict seasonal sales for businesses not interested in planning for growth.
Active Demand Forecasting
If your business is relatively new or you’re experiencing a growth phase, using the active demand forecasting model is a good option.
The active model uses a combination of historic data (if available), along with market research results, coupled with expansion plans, if available.
Short-Term
If you’re only interested in demand for the next 3-12 months, short-term demand forecasting is helpful.
The short-term model works best when you want to make quick adjustments based on real-time data and can be especially useful when looking at performance for one specific product or service.
Long-Term
The long-term demand forecasting model is used for projections more than one year into the future.
Used frequently in strategic planning, or for businesses planning for growth and expansion, the long-term model allows you to predict product performance using a combination of marketing strategies and business investments.
External
External demand forecasting uses macro forecasting by following current trends.
The external model also addresses supply chain issues such as shortages, allowing you to factor those trends into your forecast.
If your business is largely dependent on outside sources, this is an important model that should be incorporated into your demand forecasting.
Internal
Internal demand forecasting allows you to examine your internal resources to determine whether you have the resources needed should the demand for products and services grow.
For small business owners with limited staff, the internal model can be useful in determining whether you have the bandwidth to cope with burgeoning sales should demand for your products or services increase.
Demand Forecasting Methods
Demand forecasting methods should be chosen based on the type of business you own and the information that’s needed.
These are common demand forecasting methods that are used, with each method providing a different level of detail.
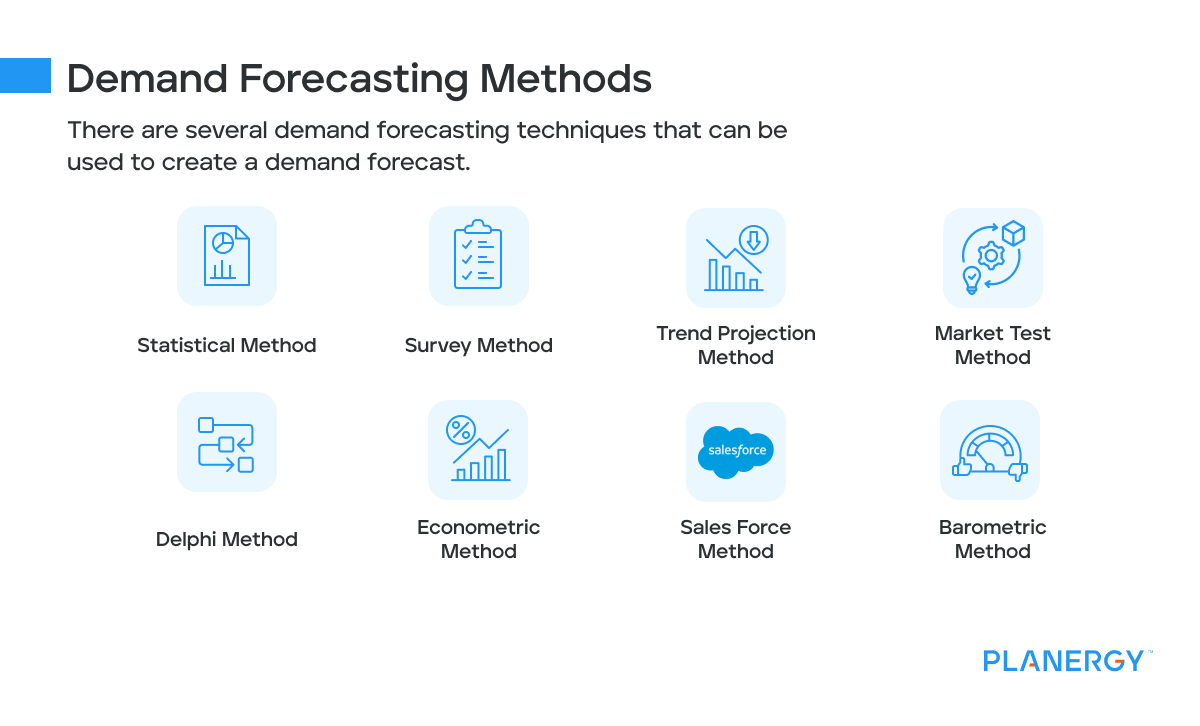
Statistical Method
The statistical method of demand forecasting is one of the easiest to use since it uses historical data when creating the demand forecast.
Survey Method
The survey method can provide vital information for a business by gathering data from a variety of stakeholders including current and potential customers.
Data is retrieved using a variety of tools including telephone and online surveys and focus groups.
This information is then factored into future predictions based on the responses received and how easily the business can incorporate those requests into its business plan.
Trend Projection Method
The trend projection method is commonly used by existing businesses that want to predict future demand by analyzing past trends.
While this method works well for ongoing trends, results can be disrupted by market fluctuations or newly imposed government regulations that can directly impact the current trend.
Market Test Method
The market test method is a good option for larger businesses that can launch a new product or service in a limited area and analyze results before a full launch.
The market launch method can provide good feedback and allow businesses to make adjustments before offering the product or service widely.
Unfortunately, it’s also an expensive method and the results from the limited launch may not reflect accurate demand in other areas.
Delphi Method
The Delphi method is primarily used by very large businesses as a way to determine product demand.
This method uses expert opinions, collecting data from each expert, and then compiling that information into a demand prediction.
The Delphi method is usually not a cost-effective method for newer businesses or those with a limited budget.
Similar to the Delphi method is the expert method, which gathers the opinions of experts in a relevant field through the use of surveys or interviews.
Econometric Method
The econometric method uses both historic sales data and newer market research results.
The econometric method is an excellent choice for a business with a long sales history but would not be useful for those with limited sales data available.
Sales Force Method
The sales force method uses the experience of your current sales team, who are in a much better position to analyze consumer behavior and customer needs.
Being familiar with demand trends can result in more accurate sales forecasting.
Your sales team is also in a better position to identify consumer demand to better predict future sales.
Barometric Method
The barometric method predicts future product demand by examining a host of external factors such as economic status, current market trends, and industry-specific desires.
The barometric method can be useful for newer businesses since it relies on outside factors, not past sales data.
How Is Demand Forecasting Done?
If you’re ready to create a demand forecast for your business but aren’t quite sure where to begin, the following steps can help guide you through the process.
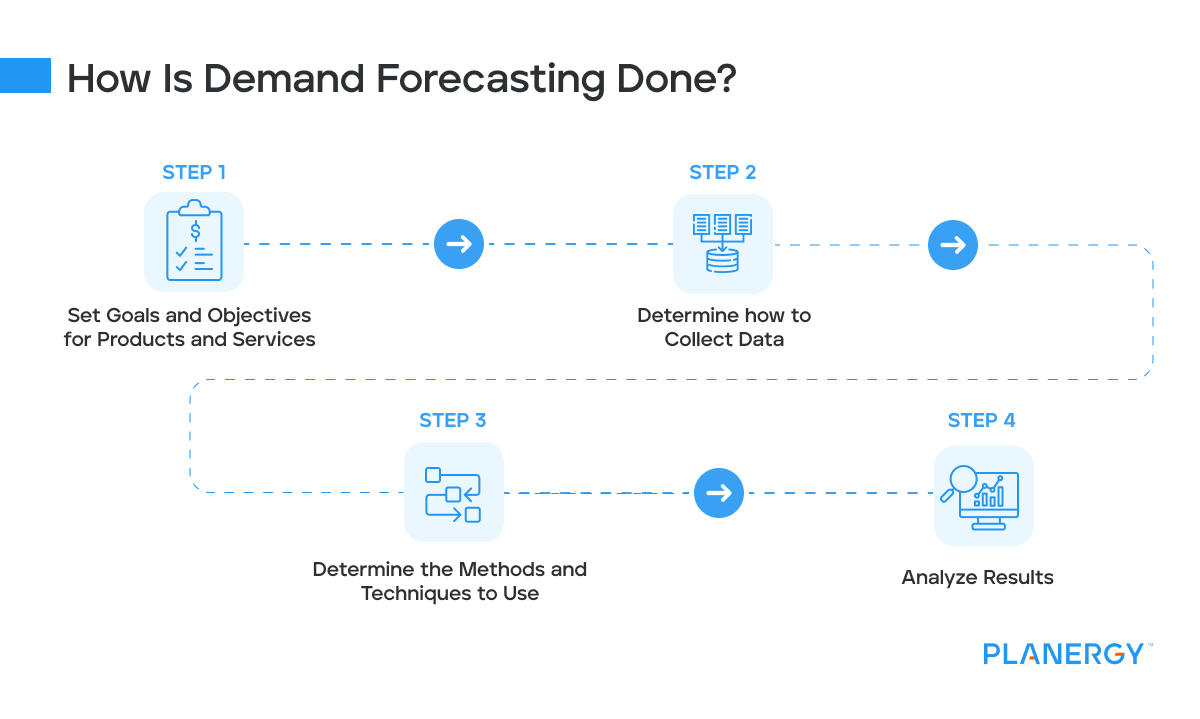
Set Goals and Objectives for Products and Services
Before you can begin the necessary research and data collection, you’ll first have to determine what information you’re interested in obtaining.
If you’re only interested in historical data, you can determine whether you wish to include the previous year’s totals or use the last two to three years of data.
If you’re looking to expand your business to a new market, you’ll want to collect data from marketing campaigns to determine demand levels.
Determine How To Collect Data
Collecting data can be challenging, depending on the information you’re looking to obtain.
If you’re interested in obtaining historical data, you can begin to gather information through financial statements.
If you’re looking to obtain outside data, you’ll need to determine what method(s) you wish to use.
For instance, if you’re interested in obtaining customer feedback, you’ll have to create and distribute surveys for your current customers.
In other cases, you may need to engage experts in the field in which you’re looking to obtain additional data.
Determine the Methods and Techniques To Use
After gathering preliminary data, you’re ready to determine what method and techniques you’re going to utilize to complete demand forecasting.
It’s likely that a variety of methods and techniques will be used, depending on the size and scope of your company and whether your business is well-established or is still in the start-up phase.
Once you’ve applied the appropriate techniques and methods to the data you’ve collected, you’re ready to begin generating a demand forecast.
Depending on the information desired you can choose to use the quantitative method that utilizes historical sales information to more accurately predict demand, while the qualitative method uses outside information to predict demand.
Analyze Results
When beginning result analysis, examine results against your original goals and objectives.
Doing so allows you to see if you have the information, you need or if you should continue to apply other methods and techniques to your forecast. In addition, be sure to ask yourself the following questions:
- Are you confident with the results or do you need to do further data collection?
- What will change for your business if your assumptions are inaccurate?
- Do the results appear to be consistent, or do they present an anomaly not previously accounted for?
Taking a closer look at these questions can help you refine your results.
What Is an Example of a Demand Forecast?
Creating a demand forecast can be a relatively simple process or could take a significant amount of time.
For our first example, we’ll look at a bakery trying to determine what supplies they must purchase to meet customer demands for the upcoming month.
Because graduation is in late spring or early summer, the bakery will need to factor in those outside conditions along with any historical data from the previous year if available to determine the level of baking supplies needed for the upcoming month.
The next example involves an automotive parts business that is looking to expand into new territory.
While they can look at historic sales at their other locations, the best way to accurately prepare a demand forecast is to conduct surveys in the area(s) where they wish to expand, asking potential customers what products or services they’re interested in.
What Is Demand Forecasting in the Supply Chain?
Both seasonality and supply chain management play an important role in demand forecasting.
If you look at the first example of a demand forecast above, you’ll be able to understand the importance of proper supply chain management.
Because the bakery was estimating how many cakes and desserts they would have to make for the upcoming month, it’s essential that they properly manage their supply chain as well.
Doing so ensures that there are enough products on hand to fulfill orders and prevent shipping disruptions without having a surplus supply left over at the end of the month.
How Does Demand Forecasting Impact Inventory Management?
Similar to supply chain management, a business must be able to accurately predict demand for products for an upcoming period without ending up with surplus inventory.
One of the ways to do this is through proper inventory planning, which includes a complete analysis of historical inventory movement for the previous period.
However, other outside factors need to be considered when managing inventory including increased or decreased competition, seasonal buying requirements, upcoming special events, and unexpected situations.
However, even taking all of these factors into consideration, it’s impossible to guarantee that a business won’t be stuck with unmovable inventory or find themselves managing backorders because of product shortages.
What Factors Influence Demand Forecasting Accuracy?
Even if you spend a lot of resources obtaining data, there’s still no guarantee that your demand forecast will be accurate.
This is because several outside factors can directly impact the accuracy of your demand forecast.
These factors include:
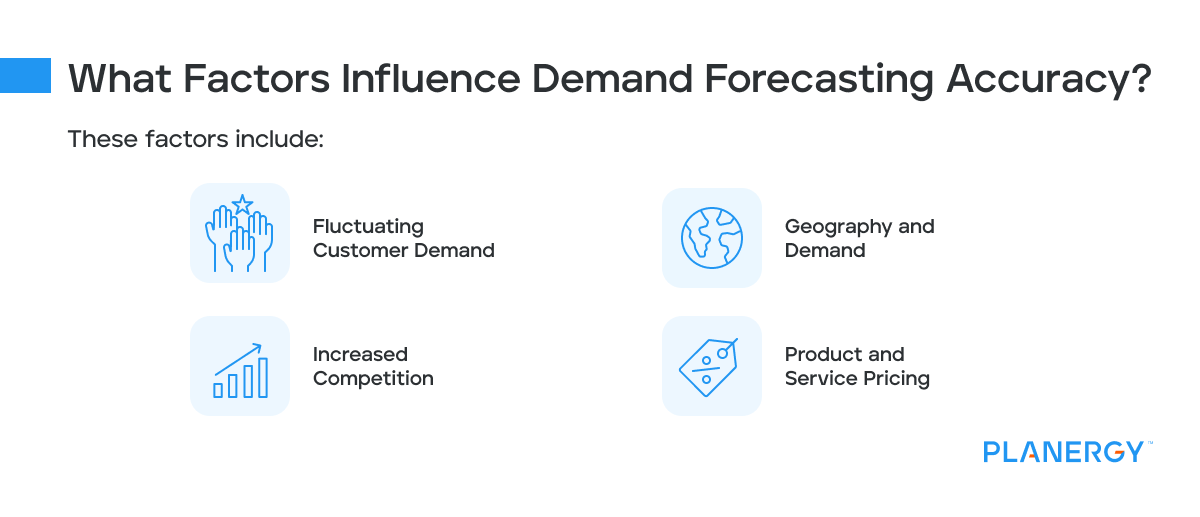
Fluctuating Customer Demand
If you own a seasonal business, you’re generating the majority of your sales during a specific period.
For example, if you own an ice cream shop, you may have good year-round business, but it’s likely that sales increase during the summer months.
However, if the economy is suffering, travel and tourism levels may decline, impacting sales for the summer months.
Increased Competition
No matter what niche your business may fall into, you’re always going to have to deal with the competition, which can impact both new and well-established businesses.
New businesses may suffer initially because it takes time to build trust and loyalty, while existing businesses may suffer if they’ve done nothing to update or freshen up their offerings.
Geography and Demand
When starting a new business, it can be difficult to gauge customer support and demand for a particular area.
If your goods and services and not limited to a specific location, this shouldn’t be an issue, but even with the proper demand forecasting completed, it’s important to remember that results obtained from one area do not necessarily translate to another seamlessly.
Product and Service Pricing
There’s a strategic reason why some businesses only choose to do business in specific areas.
For example, a luxury car dealership would likely open in an area where per-capita income levels are higher than average.
Pricing is also important for start-ups entering the market for the first time and facing competition from well-established businesses.
Benefits of Demand Forecasting
Whether you’re a start-up or an established business, demand forecasting can provide your business with a long list of benefits.
Better Ability to Manage Trends
Regularly reviewing historical sales data can help businesses spot buying trends and plan related tasks such as inventory and supply purchases accordingly.
Doing so eliminates costly mistakes such as surplus inventory or inventory shortages.
Having this information handy also allows you to make better staffing decisions and can help determine when to offer reduced pricing to keep customers returning.
Develop a Better Understanding of Outside Factors
While purchasing inventory and supplies is within the company’s control, many of the factors that directly impact sales are not.
These can include anything from changing market conditions, a slow economy, supply shortages, and increased competition, all factors that should be considered when creating a demand forecast.
Increased Ability To Plan for the Future
Whether your business is in the start-up phase or is experiencing a growth spurt, creating a demand forecast provides a blueprint for your business and should always include certain ‘what-if’ scenarios, such as:
- What if my supplier can no longer provide needed materials on time?
- What if competition increases?
- What if my factory burns down?
- What if there is no longer demand for my product or service?
Taking all of these ‘what-ifs’ into consideration when preparing your demand forecast can better prepare you for any future business downturns, whatever the reason.
Better Cash Flow Management
Businesses that can accurately predict product demand are in a better position to manage both incoming and outgoing cash flows.
For example, knowing that demand for your ice cream product drops in the winter months can help you better manage both income and expenses throughout the year.
Challenges of Demand Forecasting
For all of the benefits demand forecasting can provide a business, the process isn’t without its challenges, particularly for newer businesses that do not have historical sales data available.
Other challenges include using a poor inventory management system or dealing with sub-par supply chain management, all of which directly impact demand forecast accuracy.
Automation Is the Key to Accurate Demand Forecasting
For a company to benefit from a demand forecast, the forecast must be completed in real-time, using the most accurate data available.
If you’re still using a manual inventory management system or purchasing system, it can be time-consuming to create an accurate demand forecast.
If you’re not sure how accurate your purchasing data or inventory levels are, it’s highly unlikely that your demand forecast will be accurate.
By turning to an automated system that can optimize the process by creating accurate data sets, tracking purchases, manage inventory, and customer sales, you’re increasing accuracy and enhancing your decision-making capability.
With new businesses opening every day, an increased level of competition means that you have to be able to provide the products and services that your customers expect in a timely fashion at a fair price.
Don’t let out-of-date information get in the way of making the right business decisions for your success. Start using the appropriate forecasting tools today.




