For small business owners and entrepreneurs, managing costs effectively is crucial to maintaining financial stability and maximizing profits.
Cost management involves planning, monitoring, and controlling expenses to ensure that a business operates within its budget while achieving its financial goals.
This blog post will delve into the essentials of cost management and its role in project management and provide a step-by-step guide to crafting a comprehensive cost management plan.
What is Cost Management?
Cost management is the process of planning and controlling a business or project’s budget.
It involves analyzing all costs related to operations, setting budgetary constraints, and ensuring that expenditures align with financial objectives.
Effective cost management helps businesses optimize their resources, avoid unnecessary expenses, and achieve higher profit margins.
Importance of Cost Management
Maximizing Profits
Effective cost management allows businesses to increase profitability by carefully monitoring and adjusting expenses.
Businesses can improve their bottom line by identifying areas where costs can be reduced without compromising quality or efficiency.
This might involve negotiating better terms with suppliers, streamlining operations, or cutting unnecessary expenditures.
Financial Stability
Financial stability is critical for long-term success, and cost management is vital.
By controlling expenses, businesses ensure they have sufficient funds to meet their financial obligations, such as payroll, rent, and other overhead costs.
This stability allows for more strategic investments and weathering economic downturns.
Budget Adherence
Maintaining projects within their allocated budget is essential for avoiding cost overruns and ensuring project success.
Cost management provides a framework for setting realistic budgets, monitoring actual spending, and making necessary adjustments to keep projects on track.
Adhering to the budget prevents financial strain and builds trust with stakeholders and clients.
Cost Management in Project Management
Cost management is vital to ensure that projects are completed within budget.
It involves estimating costs, setting budgets, and controlling expenses throughout the project lifecycle.
The 4-Step Cost Management Process
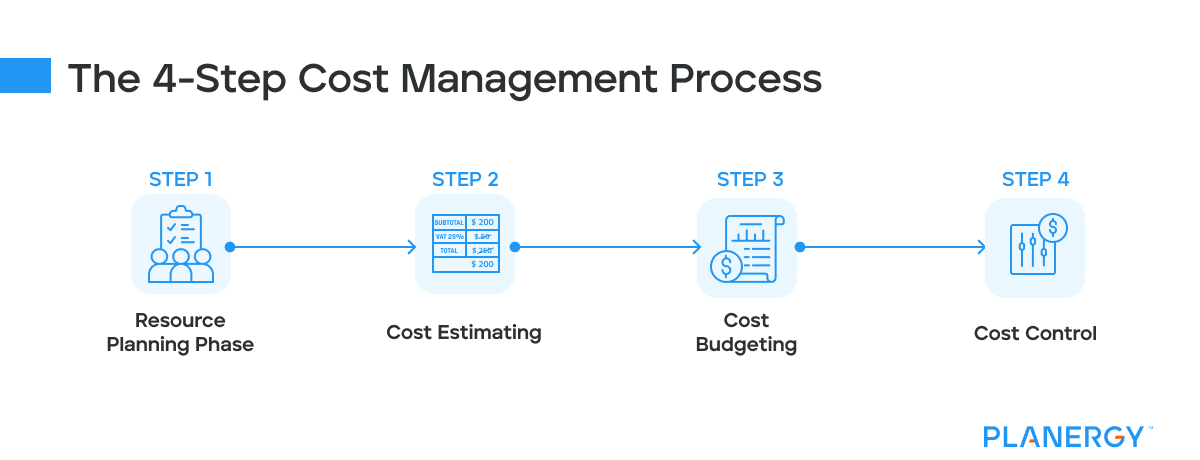
Resource Planning Phase
Resource planning involves identifying all the resources needed for a project, including personnel, equipment, materials, and other essential items.
It helps to develop a work breakdown structure (WBS) as part of the project planning process.
This provides a high level visual overview of the project. By breaking it into smaller pieces, you can get a better idea of the deliverables, the team members, and the cost of each element to get a more accurate total cost.
By estimating the quantities and costs of these resources, businesses can create a comprehensive plan that outlines what is required to complete the project successfully.
This step ensures that all necessary resources are available when they are needed and helps prevent delays and cost overruns.
Cost Estimating
Cost estimating is approximating the costs required to complete project activities.
This involves using historical data, expert judgment, and statistical methods to create accurate estimates.
Cost estimating helps set realistic budgets and provides a basis for comparing actual costs against planned expenditures.
Accurate cost estimates are crucial for effective cost management and budget adherence.
Cost Budgeting
Cost budgeting involves allocating the estimated costs to individual work packages and establishing a cost baseline.
The cost baseline is a reference point for measuring performance and tracking progress.
By breaking down the overall budget into smaller, manageable components, businesses can monitor spending more effectively and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
Cost Control
Cost control is the ongoing process of monitoring and managing cost variances from the baseline.
This involves tracking actual spending against the budget, identifying deviations, and implementing corrective actions when necessary.
Effective cost control helps businesses stay within budget and efficiently use resources. It also allows for timely adjustments to address any issues arising during the project.
Tools Used in Cost Management
Cost Estimation Software
Cost estimation software, such as Microsoft Project or Primavera, provides tools for accurately estimating project costs.
These tools offer features like templates, historical data analysis, and cost modeling, making it easier to develop precise estimates.
By leveraging these tools, businesses can improve the accuracy of their cost estimates and reduce the risk of budget overruns.
Budgeting Tools
Budgeting tools, including spreadsheets and specialized budgeting software, help businesses allocate and monitor budgets effectively.
These tools provide functionalities for creating detailed budgets, tracking expenditures, and generating financial reports.
By using budgeting tools, businesses can better see their financial performance and make more informed decisions.
Earned Value Management (EVM)
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a technique that combines scope, schedule, and resource measurements to assess project performance and progress.
EVM provides a comprehensive view of a project’s performance relative to its budget and schedule, allowing for early identification of potential issues.
By integrating EVM into cost management processes, businesses can enhance their ability to control costs and deliver projects on time and within budget.
Key Components of an Effective Project Cost Management System
Effective project cost management is essential for ensuring that projects are completed within budget while maintaining quality and meeting deadlines.
A well-structured cost management system helps organizations plan, estimate, allocate, and control costs throughout the project lifecycle.

Budgeting
Budgeting is the foundation of an effective cost management system.
It involves creating a financial plan that outlines all expected costs and revenues for a specific period.
A well-defined budget provides a roadmap for managing expenses and helps businesses prioritize spending. It also serves as a benchmark for measuring actual performance and making informed financial decisions.
Consider the project resources, types of costs, and more as you develop the budget.
It’s always a good idea to add some contingency reserves into the budget so you have a bit of wiggle room if there’s an overage on one area.
This helps to be sure you can still adhere to the project schedule and overall budget.
You can estimate project expenses in four ways, and often, projects require using a combination of these methods.
Since each approach is associated with risk and opportunity management and detailed estimates are time-consuming, you must determine which projects are worth spending more time on accurate and detailed estimates.
Bottom-Up Estimating
The bottom-up method involves estimating the costs of individual tasks or components of a project and then aggregating these estimates to arrive at a total project cost.
This approach requires detailed knowledge of each task, including labor, materials, equipment, and other resources.
Top-Down Estimating
The top-down method involves estimating the total project cost based on historical data, expert judgment, or analogous projects and then breaking it down into smaller components.
This approach starts with a high-level overview and drills down into specific details.
Matrix Estimation Method
The matrix method combines elements of both the bottom-up and top-down approaches.
It uses detailed task-level estimates but also incorporates higher-level adjustments based on historical data and expert judgment.
Analogous Estimating
The analogous method involves estimating costs based on the costs of similar projects you’ve already completed.
This method relies on the assumption that historical data from comparable projects can provide a reasonable basis for new estimates.
So, if there have been major changes in the cost of project resources due to an increase in raw material costs, labor costs, or additional variable costs, it may not be the best way to ensure a successful project budget.
Forecasting
Forecasting predicts future expenses based on historical data, trends, and market conditions.
Accurate forecasting enables businesses to anticipate potential cost fluctuations and proactively adjust their budgets.
By regularly updating forecasts, businesses can stay ahead of financial challenges and remain aligned with their long-term goals.
Monitoring
Regularly monitoring actual costs and resource management against the budget is essential for effective cost management.
This involves tracking expenditures in real time, identifying variances, and analyzing the reasons behind them.
Continuous monitoring allows businesses to detect potential issues early and take corrective actions to stay within budget.
It also provides valuable insights into spending patterns and areas for improvement.
Reporting
Providing detailed reports on financial performance is crucial for transparency and accountability.
Regular reporting helps stakeholders understand how well a business manages its costs and whether it is meeting its financial objectives.
Reports should include key metrics, such as actual vs. budgeted costs, cost variances, and progress toward financial goals.
Clear and concise reporting facilitates informed decision-making and supports effective cost management.
Creating a Cost Management Plan: Step-by-Step Guide
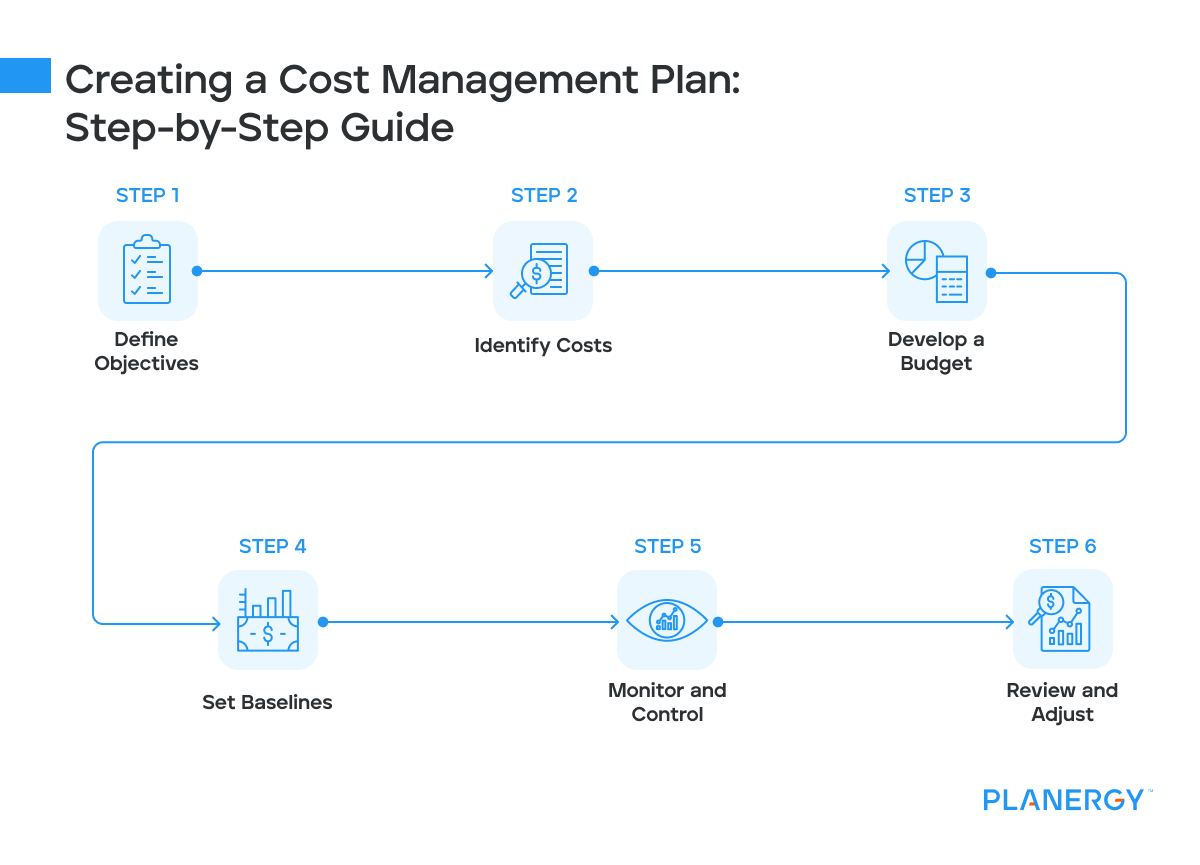
Define Objectives
Clearly outlining the financial goals of your project or business is the first step in creating a cost management plan.
These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Defining clear objectives provides direction and sets the foundation for all subsequent cost management activities.
Identify Costs
Listing all potential direct and indirect costs is essential for developing an accurate budget.
Direct costs are those directly associated with a project or business activity, such as labor and materials.
Indirect costs, on the other hand, are not directly tied to a specific project but are necessary for overall operations, such as utilities and administrative expenses. Identifying all potential costs ensures that no expenses are overlooked.
Develop a Budget
The next step is to create a detailed budget that includes cost estimates for each activity.
This involves allocating resources to different tasks and setting spending limits.
A well-developed budget provides a clear financial plan that guides spending decisions and helps ensure that resources are used efficiently. It also serves as a baseline for measuring actual performance.
Set Baselines
Establishing cost baselines is crucial for measuring actual performance against planned performance.
A cost baseline is a fixed reference point representing the approved budget at a specific point in time.
By comparing actual costs to the baseline, businesses can identify variances and assess whether they are on track to meet their financial goals.
Monitor and Control
Continuously tracking expenses and implementing corrective actions is essential for staying within budget.
This involves regular monitoring of actual costs, comparing them to the budget, and taking action to address any deviations.
Effective monitoring and control help ensure that resources are used efficiently and that financial objectives are met.
Review and Adjust
Regularly reviewing the cost management plan and making necessary adjustments is crucial for ongoing success.
This involves evaluating the effectiveness of cost management strategies, identifying areas for improvement, and updating the plan to reflect changing circumstances.
Regular reviews ensure that the cost management plan remains relevant and aligned with business goals.
Progress Reporting and Earned Value Management (EVM)
Progress Reporting
Regular progress reporting is essential in cost management.
These reports provide insights into how well a project or business performs financially and whether it is on track to meet its budgetary goals.
Progress reports should include key metrics, such as actual vs. budgeted costs, cost variances, and progress toward financial objectives.
Clear and concise reporting facilitates informed decision-making and supports effective cost management.
Earned Value Management
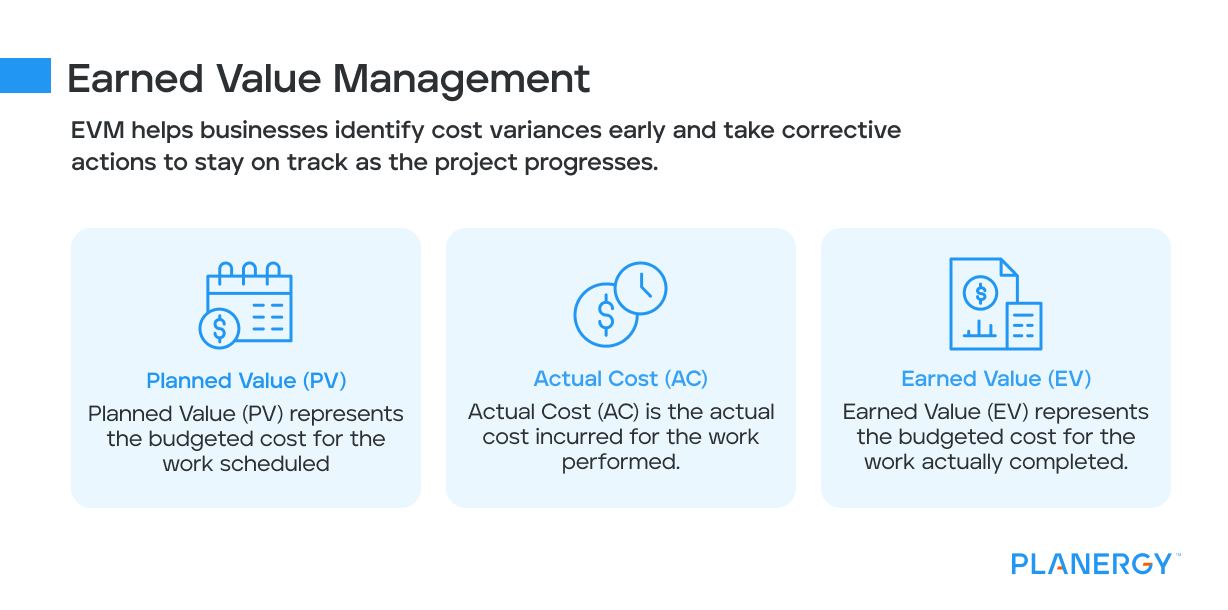
Earned value management is a powerful tool used in cost control. It integrates project scope, cost, and schedule measures to provide accurate forecasts of project performance.
EVM helps businesses identify cost variances early and take corrective actions to stay on track as the project progresses.

Planned Value (PV)
Planned Value (PV) represents the budgeted cost for the work scheduled.
It provides a baseline for measuring project performance and helps businesses assess whether they are on track to meet their financial objectives.
Actual Cost (AC)
Actual Cost (AC) is the actual cost incurred for the work performed.
Comparing AC to PV helps businesses identify cost variances and assess whether they stay within budget.
Earned Value (EV)
Earned Value (EV) represents the budgeted cost for the work actually completed.
By comparing EV to PV and AC, businesses can assess overall project performance and take corrective actions as needed.
Maximizing Profitability and Financial Stability Through Effective Cost Management
Effective cost management is essential for small business owners and entrepreneurs to maximize profits and ensure financial stability.
By understanding the cost management process and implementing a structured plan, businesses can maintain control over their finances and achieve their financial goals.