Budgeting is a critical financial planning and management aspect for individuals, businesses, and organizations.
Among the various types of budgeting, strategic budgeting stands out as a powerful tool for achieving long-term financial goals.
This comprehensive guide will delve into strategic budgeting, its importance, the steps involved in creating a strategic budget, benefits, challenges, best practices, and help identify differences between forecasting and budgeting.
What is Strategic Budgeting?
Strategic budgeting is a process that combines budgeting with strategic planning, aligning an organization’s financial resources with its long-term objectives.
It focuses on allocating resources effectively, prioritizing investments, and ensuring financial stability while pursuing growth and innovation.
Different Types of Budgeting Methods
There are various different types of budgets and budgeting models in accounting.
Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting is a traditional approach to budget planning that involves taking the previous year’s annual budget and adjusting it based on factors such as inflation, cash flow, or other changes in the organization’s financial landscape.
This method is simple to implement and maintain, relying on historical data and relatively minor adjustments.
However, incremental budgeting may not account for changing priorities, short-term expenditures, or new opportunities, limiting its effectiveness in some situations.
Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-based budgeting is a more rigorous approach that requires every expense to be justified each budgeting period, starting from zero.
This method encourages efficiency and reduces unnecessary spending by forcing organizations to evaluate each expenditure and its contribution to its goals carefully.
While zero-based budgeting can lead to more effective resource allocation, it can be time-consuming and challenging to implement, as it requires a comprehensive review of all expenses during each budgeting cycle.
Activity-Based Budgeting
Activity-based budgeting focuses on the cost of activities and processes required to achieve specific objectives.
By examining the relationship between costs and outcomes, activity-based budgeting helps organizations identify inefficiencies, allocate resources more effectively, and improve overall financial performance.
This type of budgeting can be complex and require significant data analysis, making it more suitable for organizations with well-defined processes and the ability to gather detailed cost information.
Strategic Budgeting
Strategic budgeting, as previously mentioned, is a method that combines strategy and budget planning, emphasizing long-term objectives and resource allocation.
This approach ensures that an organization’s financial resources are aligned with its overarching goals, promoting growth, innovation, and financial stability.
By focusing on long-term priorities and investments, strategic budgeting helps organizations make informed decisions about resource allocation and adapt to changing market conditions.

Why are Budgeting Strategies Important?
Budgeting strategies like strategic budgeting help organizations make informed decisions about resource allocation, prioritize investments, and ensure financial stability.
They provide a roadmap for achieving long-term goals, promoting growth and innovation while managing risks and uncertainties.
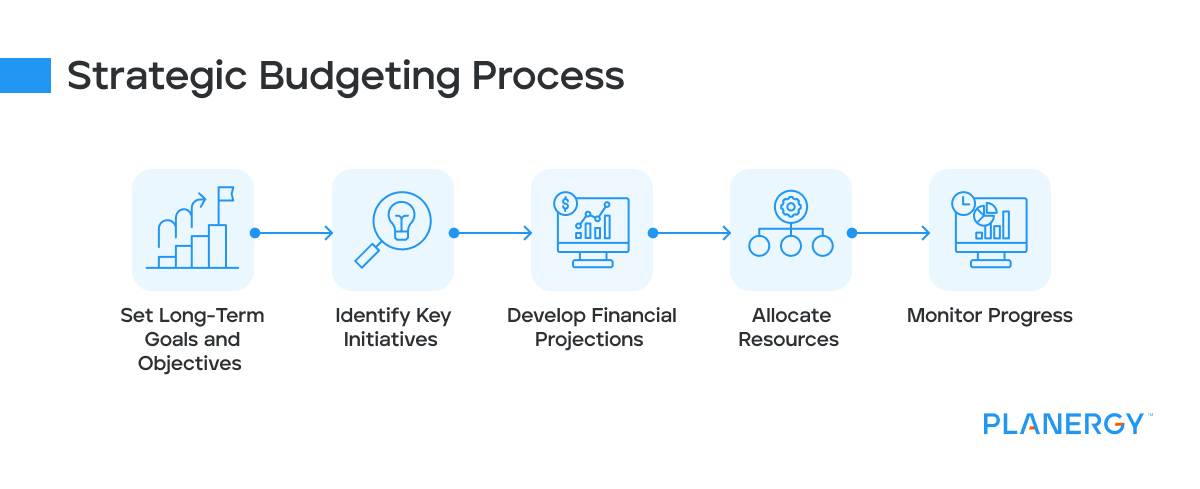
The Strategic Budgeting Process
Creating a strategic budget involves the following steps:
Set Long-Term Goals and Objectives
Begin the strategic budgeting process by defining your organization’s long-term goals.
These goals can include market expansion, new product development, revenue growth, or other objectives that drive your organization’s success. Setting clear and measurable goals will provide the foundation for the rest of the budgeting process.
Identify Key Initiatives
With your long-term objectives, determine the strategic initiatives required to achieve these goals.
Such initiatives may include marketing campaigns, research and development projects, or hiring new talent. Identifying key initiatives helps ensure that your budget is focused on activities that contribute directly to your organization’s long-term success.
Develop Financial Projections
Next, develop financial projections for each identified initiative. Estimate the costs associated with each initiative and project revenues based on market trends, historical data, and growth expectations.
Accurate financial projections are essential for allocating resources effectively and setting realistic expectations for the outcome of each initiative.
Allocate Resources
With financial projections in hand, allocate financial resources to each initiative. Prioritize initiatives with the highest potential impact on your long-term objectives, ensuring that your budget is aligned with your organization’s goals.
Resource allocation is a critical step in the strategic budgeting process, as it determines where your organization will invest its time, effort, and money.
Monitor Progress
Finally, regularly review your strategic budget versus actual expenditure and monitor progress towards your long-term objectives. Compare actual results with your projections and adjust as needed to stay on track.
Monitoring progress is crucial for maintaining accountability, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring that your strategic budget remains aligned with your organization’s goals. You can make data-driven decisions that drive your organization forward by consistently evaluating your budget’s performance.
Benefits of Strategic Budgeting
Aligning Resources with Long-Term Strategic Goals
Strategic budgeting allows organizations to focus on their most important initiatives, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.
By aligning financial resources with long-term goals, organizations can prioritize investments that contribute directly to their success, making the most of their available resources.
Encouraging Innovation and Growth
One of the key benefits of strategic budgeting is its ability to promote investment in new opportunities and support long-term growth.
Organizations can continually evolve, adapt, and stay competitive in their respective industries by identifying and prioritizing initiatives that drive innovation and expansion. An agile business can be ready to seize opportunities.
Improving Decision-Making
Strategic budgeting provides a clear roadmap for achieving an organization’s objectives, which helps improve decision-making at all levels.
With a well-defined budget, organizations can make informed decisions about investments and resource allocation, ensuring that every financial decision supports their long-term goals and overall strategic vision.
Enhancing Financial Stability
Strategic budgeting contributes to an organization’s financial health and stability by prioritizing investments and managing business risks.
Organizations can identify areas where resources may be better allocated, reduce unnecessary spending through strong budgetary control and spend control, and ensure they are prepared to weather any financial challenges that may arise.
This proactive approach to financial management helps organizations maintain a strong financial position and achieve their long-term objectives.

Challenges of Strategic Budgeting
Ensuring Accurate Projections
One of the main challenges of strategic budgeting is developing accurate financial projections, which can be difficult in uncertain or rapidly changing markets.
Organizations must carefully analyze historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors to create realistic budget forecasting projections that accurately reflect their long-term goals and objectives.
When planning your projections you should also ensure you are budgeting for variable expenses, if not planned for these can easily blow your budget.
Inaccurate projections can lead to poor decision-making and resource allocation, ultimately undermining the effectiveness of the strategic budget.
Fostering Collaboration
Creating a strategic budget requires input and cooperation from various organizational departments and stakeholders. This involves other departments collaborating effectively with finance.
This collaboration can be challenging, as different departments may have competing priorities, differing opinions on resource allocation, or varying levels of understanding about the organization’s overall strategy.
To overcome this challenge, organizations must foster a culture of open communication, shared goals, and commitment to the strategic budgeting process.
Maintaining Ongoing Monitoring
Effective strategic budgeting demands regular reviews and adjustments, which require time and effort from all involved parties.
Organizations must continually monitor their progress, compare actual results with projections, and make necessary adjustments to stay on track.
Having real-time spend visibility, carrying out budget variance analysis, reviewing spend analysis on procurement activities, and following budget reporting best practices by using a dedicated spend management software that incorporates business budgeting software, like PLANERGY, can help.
This ongoing monitoring can be time-consuming, especially if managed manually, but it is crucial for ensuring that the strategic budget remains aligned with the organization’s long-term goals and objectives.
Implementing tools and processes to streamline budget monitoring and reporting can help mitigate this challenge and promote a more efficient approach to strategic budgeting.

Regardless of business size, the right budgeting strategy can be the difference between success and failure.
Best Practices for Strategic Budgeting
Involving the Leadership Team and All Stakeholders
One of the most important best practices for strategic budgeting is to engage key stakeholders in the business budget planning process.
This ensures buy-in and commitment from all parties involved, fostering collaboration and effective decision-making.Encourage open communication, solicit input and feedback, and ensure that all stakeholders understand the organization’s long-term goals and the role of the strategic budget in achieving those objectives.
Leveraging Historical Data and Market Research
Leveraging historical data and market research to create accurate financial projections and assumptions is crucial.
Analyze past performance, market trends, and industry insights to make informed decisions about resource allocation and expected outcomes.
You can increase your strategic budget’s accuracy and effectiveness by grounding your strategic budget in data-driven insights.
Using the Right Tools
It’s important to use the right budgeting tools, as they play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and efficacy of the budgeting process.
Effective tools streamline data management, facilitate stakeholder collaboration, and allow organizations to monitor their financial performance easily.
While Excel might be an excellent option initially for smaller companies, its limitations become apparent in larger and more complex organizations.
As organizations grow, they require more advanced budgeting solutions and controls to handle increased data volume, automate repetitive tasks, and provide real-time insights into financial performance.
By investing in the right budgeting tools, organizations can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their budgeting process, ultimately leading to better decision-making, resource allocation, and financial success.
Being Realistic and Conservative
When developing financial projections and assumptions, it’s essential to be realistic and conservative.
Avoid overly optimistic projections that may be difficult to achieve, and instead, focus on attainable goals that align with your organization’s goals for the coming year and long-term objectives.
Additionally, build contingencies into your budget to account for unforeseen events or challenges, ensuring your organization is prepared to adapt and respond to changing circumstances.
Implementing a Rolling Budget
Instead of relying on a traditional annual budget, consider implementing a rolling budget combined with rolling forecasts that is continually updated and extended as new information becomes available.
A rolling budget allows organizations to respond more quickly to changes in the market or their financial situation, promoting agility and adaptability.
Regularly updating and revising your strategic budget ensures it remains aligned with your organization’s evolving goals and priorities.

Budgeting vs. Forecasting: Key Differences
Budgeting: Creating a Financial Plan
Budgeting is the process of creating a detailed financial plan for a specific period, usually a fiscal year, and allocating resources to achieve specific organizational goals.
The budget serves as a roadmap for financial decision-making, guiding how funds should be spent and outlining expected income and expenditures.
Budgets are typically fixed, meaning they remain relatively unchanged throughout the budget period, and are used to assess performance by comparing actual results against the planned figures.
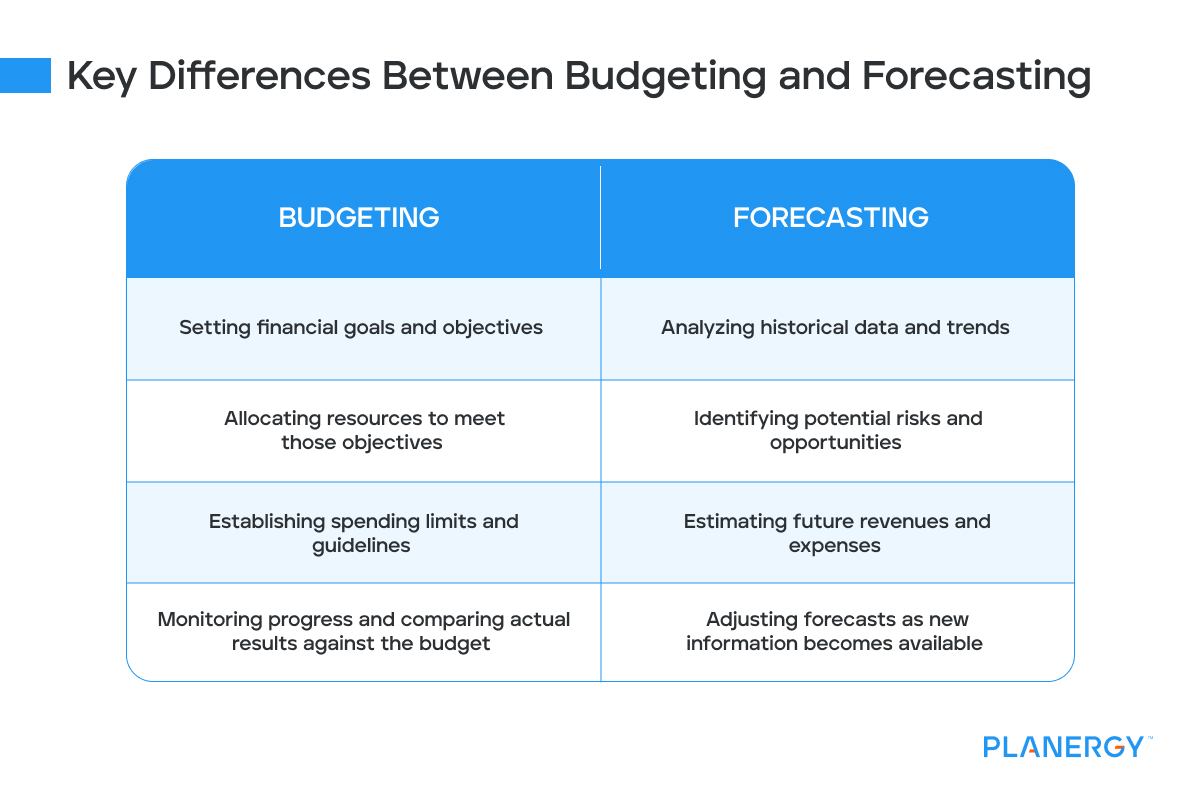
Key aspects of budgeting include:
- Setting financial goals and objectives
- Allocating resources to meet those objectives
- Establishing spending limits and guidelines
- Monitoring progress and comparing actual results against the budget
Forecasting: Estimating Future Financial Outcomes
In contrast, forecasting involves estimating future financial outcomes based on historical data, market trends, and various assumptions. Spend forecasting helps inform budget planning.
Forecasts are more flexible than budgets, as they are continually updated and revised as new information becomes available or circumstances change.
Forecasting helps organizations anticipate future performance, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make proactive decisions to maximize success.
Key aspects of forecasting include:
- Analyzing historical data and trends
- Identifying potential risks and opportunities
- Estimating future revenues and expenses
- Adjusting forecasts as new information becomes available
Embrace Strategic Budgeting for Long-Term Success
Strategic budgeting is a powerful tool for aligning an organization’s financial resources with its long-term objectives.
By following the steps outlined in this guide and implementing best practices, businesses and organizations can effectively create and manage their operating budgets, achieving growth, innovation, and financial stability.




